First Grade Common Core State
Standard
-
Aligned
First Grade Math Beginning
& End of Year Assessments
Nordonia Hills Math SLO

Operations and Algebraic Thinking 1.OA
A. Represent and solve problems involving addition and subtraction.
1.OA.1 Use addition and subtraction within 20 to solve word problems involving situations
of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart, and comparing, with unknowns in
all positions, e.g., by using objects, drawings, and equations with a symbol for the unknown
number to represent the problem. (See Glossary)
1.OA.2 Solve word problems that call for addition of three whole numbers whose sum is
less than or equal to 20, e.g., by using objects, drawings, and equations with a symbol for
the unknown number to represent the problem.
B. Understand and apply properties of operations and the relationship between addition
and subtraction
1.OA.3 Apply properties of operations as strategies to add and subtract. (Students need
not use formal terms for these properties.) Examples:
If 8 + 3 = 11 is known, then 3 + 8 = 11 is also known. (Commutative property of addition.)
To add 2 + 6 + 4, the second two numbers can be added to make a ten, so 2 + 6 + 4 =
2 + 10 = 12. (Associative property of addition.)
1.OA.4 Understand subtraction as an unknown-addend problem.
For example, subtract 10 – 8 by finding the number that makes 10 when added to 8.
C. Add and subtract within 20.
1.OA.5 Relate counting to addition and subtraction (e.g., by counting on 2 to add 2).
1.OA.6 Add and subtract within 20, demonstrating fluency for addition and subtraction
within 10. Use strategies such as counting on; making ten (e.g., 8 + 6 = 8 + 2 + 4 = 10 +
4 = 14); decomposing a number leading to a ten (e.g., 13 – 4 = 13 – 3 – 1 = 10 – 1 = 9);
using the relationship between addition and subtraction (e.g., knowing that 8 + 4 = 12, one
knows 12 – 8 = 4); and creating equivalent but easier or known sums (e.g., adding 6 + 7
by creating the known equivalent 6 + 6 + 1 = 12 + 1 = 13).
D. Work with addition and subtraction equations.
1.OA.7 Understand the meaning of the equal sign, and determine if equations involving
addition and subtraction are true or false. For example, which of the following equations
are true and which are false? 6 = 6, 7 = 8 – 1, 5 + 2 = 2 + 5, 4 + 1 = 5 + 2.
1.OA.8 Determine the unknown whole number in an addition or subtraction equation
relating to three whole numbers. For example:
8 + ? = 11, 5 = ?– 3, 6 + 6 = ?

Number and Operations in Base Ten 1.NBT
E. Extend the counting sequence.
1.NBT.1 Count to 120, starting at any number less than 120. In this range, read and write
numerals and represent a number of objects with a written numeral.
F. Understand place value.
1.NBT.2 Understand that the two digits of a two-digit number represent amounts of tens
and ones. Understand the following as special cases:
a. 10 can be thought of as a bundle of ten ones — called a “ten.”
b. The numbers from 11 to 19 are composed of a ten and one, two, three, four, five, six,
seven, eight, or nine ones.
c. The numbers 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90 refer to one, two, three, four, five, six,
seven, eight, or nine tens (and 0 ones).
1.NBT.3 Compare two two-digit numbers based on meanings of the tens and ones digits,
recording the results of comparisons with the symbols >, =, and <.
G. Use place value understanding and properties of operations to add and subtract.
1.NBT.4 Add within 100, including adding a two-digit number and a one-digit number, and
adding a two-digit number and a multiple of 10, using concrete models or drawings and
strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between
addition and subtraction; relate the strategy to a written method and explain the reasoning
used. Understand that in adding two-digit numbers, one adds tens and tens, ones and ones;
and sometimes it is necessary to compose a ten.
1.NBT.5 Given a two-digit number, mentally find 10 more or 10 less than the number,
without having to count; explain the reasoning used.
1.NBT.6 Subtract multiples of 10 in the range 10-90 from multiples of 10 in the range
1090 (positive or zero differences), using concrete models or drawings and strategies based
on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and
subtraction; relate the strategy to a written method and explain the reasoning used.
Measurement and Data 1.MD
H. Measure lengths indirectly and by iterating length units.
1.MD.1 Order three objects by length; compare the lengths of two objects indirectly by
using a third object.

1.MD.2 Express the length of an object as a whole number of length units, by laying
multiple copies of a shorter object (the length unit) end to end; understand that the length
measurement of an object is the number of same-size length units that span it with no gaps
or overlaps. Limit to contexts where the object being measured is spanned by a whole
number of length units with no gaps or overlaps.
I. Tell and write time.
1.MD.3 Tell and write time in hours and half-hours using analog and digital clocks.
J. Represent and interpret data.
1.MD.4 Organize, represent, and interpret data with up to three categories; ask and answer
questions about the total number of data points, how many in each category, and how
many more or less are in one category than in another.
Geometry 1.G
K. Reason with shapes and their attributes.
1.G.1 Distinguish between defining attributes (e.g., triangles are closed and three-sided) versus
non-defining attributes (e.g., color, orientation, overall size); build and draw shapes to possess
defining attributes.
1.G.2 Compose two-dimensional shapes (rectangles, squares, trapezoids, triangles, halfcircles,
and quarter-circles) or three-dimensional shapes (cubes, right rectangular prisms, right
circular cones, and right circular cylinders) to create a composite shape, and compose new
shapes from the composite shape. (Students do not need to learn formal names such as
“right rectangular prism.”)
1.G.3 Partition circles and rectangles into two and four equal shares, describe the shares
using the words halves, fourths, and quarters, and use the phrases half of, fourth of, and
quarter of. Describe the whole as two of, or four of the shares. Understand for these
examples that decomposing into more equal shares creates smaller shares.

Beginning of Year
Pre
-
Assessment
Nordonia Hills City Schools
Math SLO / 100 points
Student:
Date:
Teacher:

Teaching Fabulous Firsties
Jan caught 2 bugs. Tim caught 4 bugs.
How many bugs did they catch in all?
_____
bugs
Show or
Tell:
©
Corinna Woita
2013
+
Bob caught 2 ants, 4 butterflies, and 1 bee.
How many bugs did he catch?
_______
bugs
Show or
Tell
1
.OA.
1
1
.OA.
2

Teaching Fabulous Firsties
There are 8 fireflies and 5 bees in the jar.
There are more _________ in the jar. How many more?_____
_
Show or
Tell:
©
Corinna Woita
2013
+
There are 10 bugs in a jar. 3 bugs crawled out.
How many bugs are left?
_______
bugs
Show or
Tell
1
.OA.
1
1
.OA.
2
Teaching Fabulous Firsties
.OA.3 Associative Property
1
Add the numbers.
©
2013
Corinna Woita
+
6
+
4
+
3
=
7
+
3
+
6
=
5
+
4
+
1
=
If you know: Then, you know:
.OA.3 Commutative Property
1
7
+
3
=
10
6
+
5
=
11
+
=
+
=
1
.OA.
4
9
-
4
=
10
-
3
=
+
=
9
+
=
10
Use a related addition fact to solve a subtraction fact

Teaching Fabulous Firsties

Is the equation true or false?
Circle your answer.
©
2013
Corinna Woita
+
Teaching Fabulous Firsties
8
-
2
=
6
4
=
6
-
3
9
+
2
=
10
5
-
3
=
2
true or false ?
true or false ?
true or false ?
true or false ?
1
7
.OA.
5
-
=
1
+
3
=
8
9
-
5
=
.OA.
8
1
Fill in the missing numbers.
Write the “Fact Family” using 3, 7, and 10
:
©
Corinna Woita
2013
+
Teaching Fabulous Firsties
1
.OA.
6
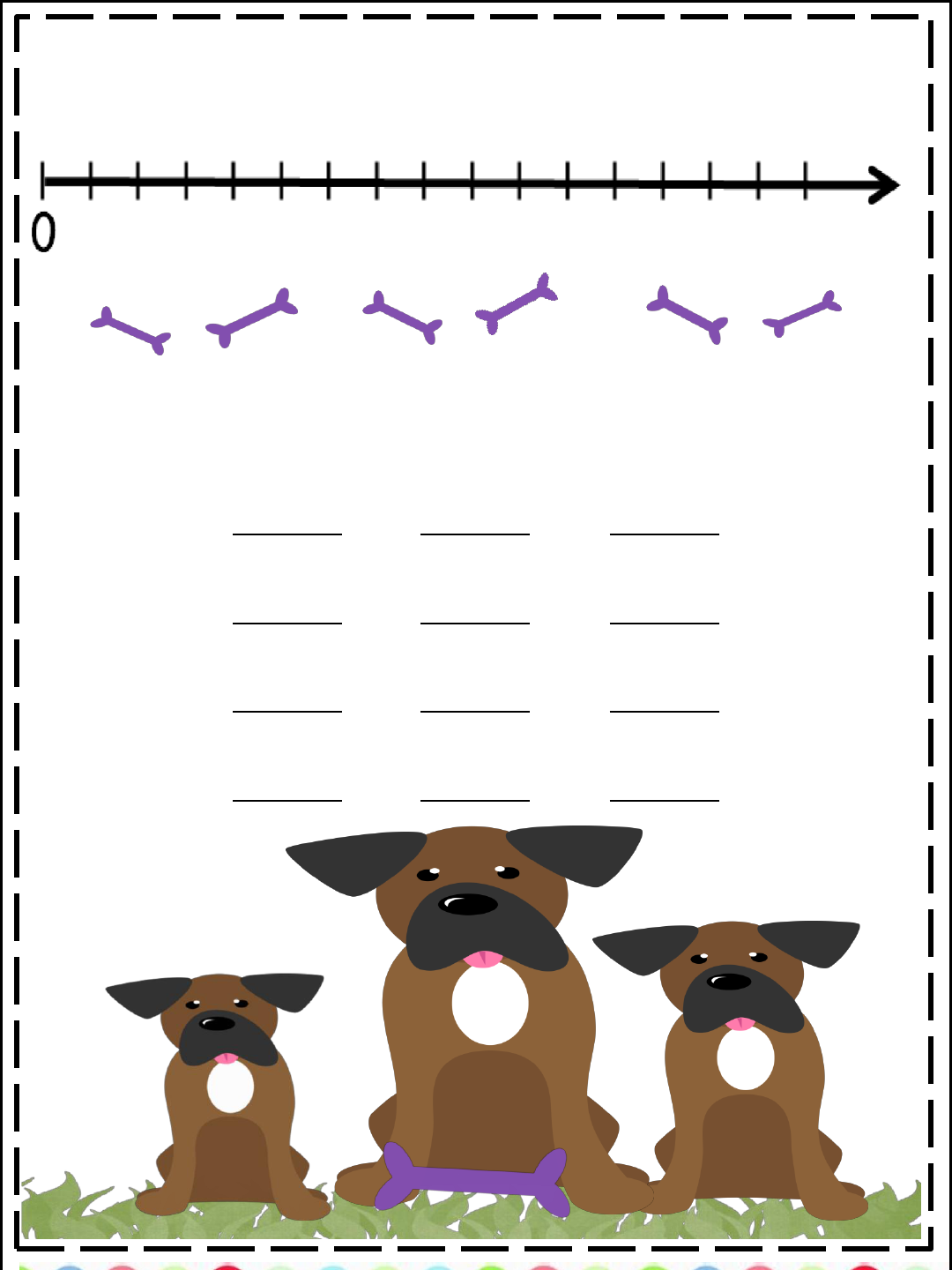
Find where the numbers
7
and
12
are on the number
line. Write the numbers where they belong .
7
10
3
+
=
+
=
-
=
-
=

1
.MD.
3
:
:
:
:
12:30
5:00
Draw hands on the analog clock.
©
2013
Corinna Woita
+
Teaching Fabulous Firsties
Write the time on the digital clock.

5
4
3
2
1
chicken
pig
cow
•
Which animal has
the
most
votes?
______________
•
Which animal has the
least
votes
?_______________
•
How
many votes does the
chicken have
?_________
•
How many more votes does the cow have than
the pig?
______
•
How many people voted in all?
______people
•
How many votes do the chicken and
cow
have
in
all?
______
Use the graph below to answer the questions
.
Our Favorite Farm Animals
4
.MD.
1
©
2013
Corinna Woita
+
Teaching Fabulous Firsties

Circle the triangles. Tell how you know.
_______________________________________
________________________________________
1
.G.
1
..
1.G.3
Draw a line to show how you and a friend can
equally share this candy bar.
©
2013
Corinna Woita
+
Teaching Fabulous Firsties

1.G..2
Cut out the squares below and glue them
together to create a larger square or
rectangle.
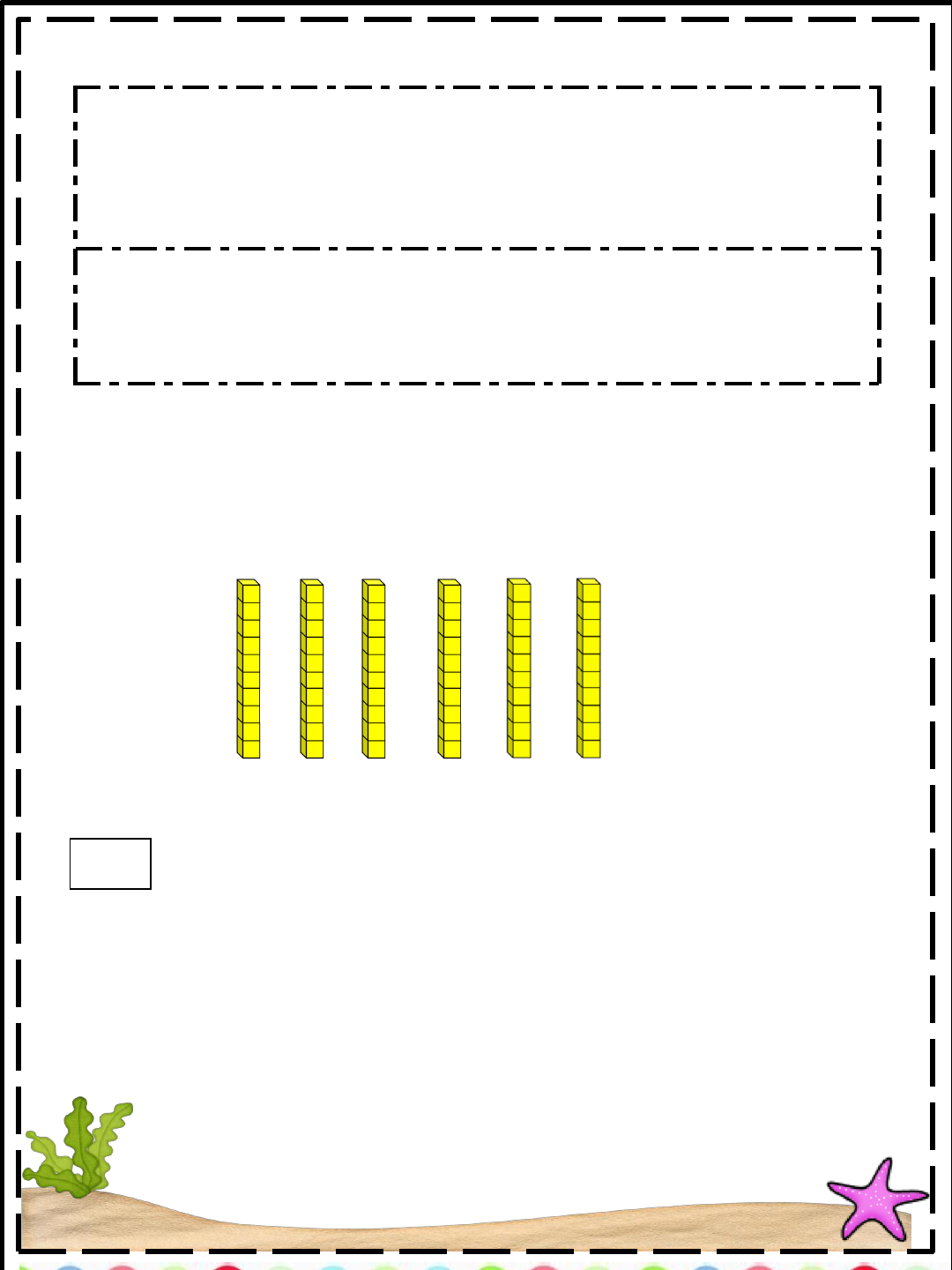
38
52
Draw Base Ten blocks to represent each number
.
©
2013
Corinna Woita
+
Teaching Fabulous Firsties
=
Solve the problems
.NBT.1
1
_____
Count the Base 10 blocks and write the number that
they represent.
.1.NBT.2a
1.NBT.2b
10 + 3 = _____
10 + 7 = ______
10 + 4 = ______

30+23=
___
+
©
Corinna Woita
2013
+
Teaching Fabulous Firsties
1
90
=
__
tens &
__
ones
=
20
__
tens &
__
ones
31
38
12
21
Fill in the correct symbol.
= <
>
49
94
90
90
Solve the addition problem.
1
.NBT .
4
1.NBT
.3

24
+13
38
-
10
56
-
23
32
+
6
Solve the problem.
You
may draw base ten blocks to help you.
©
2013
Corinna Woita
+
Teaching Fabulous Firsties
.NBT .4
1

©
Corinna Woita
2013
+
Teaching Fabulous Firsties
22
45
Fill in the number grid with
10
more, 10 less, 1 more, and 1 less.
1
.NBT.5
1
.NBT.6
Solve the subtraction problem.
Draw an X on the Base 10 blocks you subtract.
30
-
10
50
-
30

End of Year
Post
-
Assessment
Name:
Student:
Teacher:
Nordonia Hills City Schools
Math SLO

Teaching Fabulous Firsties
Pam
caught
6
bugs.
Sam
caught 4 bugs.
How many bugs did they catch in all?
_____
bugs
Show or
tell:
©
Corinna Woita
2013
+
Dan
caught
5
ants, 2 butterflies
, and
bees.
2
How many bugs did he catch?
_______
bugs
Show or
tell:
1
.OA.
1
1
.OA.
2

Teaching Fabulous Firsties
There are 18 bugs in a jar. 9 bugs crawled away.
How many bugs are left in the jar?
_____
bugs
Show or
tell:
©
Corinna Woita
2013
+
Tim caught 16 fireflies and 9 bees. He has fewer
____________________. How many more
fireflies than bees does he have in the jar?
Show or
tell:
1
.OA.
1
1
.OA.
2

Teaching Fabulous Firsties
.OA.3 Associative Property
1
Add the numbers.
©
2013
Corinna Woita
+
2
+
5
+
2
=
8
+
2
+
3
=
2
+
4
+
1
=
If you know: Then, you know:
.OA.3 Commutative Property
1
8
+
1
=
9
2
+
3
=
5
+
=
+
=
1
.OA.
4
10
-
8
=
8
-
3
=
+
=
10
+
=
8
Use a related addition fact to solve a subtraction fact

Teaching Fabulous Firsties
Count by 2’s
Count by 10’s

Is the equation true or false?
Circle your answer.
9
-
7
=
2
6
=
9
-
3
7
+
8
=
16
8
-
5
=
3
true or false ?
true or false ?
true or false ?
true or false ?
1
7
.OA.
8
-
=
4
+
2
=
12
11
-
5
=
.OA.
8
1
Fill in the missing numbers.

Write the “Fact Family” using
6
,
9
,
and
15
:
©
2013
Corinna Woita
+
Teaching Fabulous Firsties
1
.OA.
6
Find where the numbers
35
and
44
are on the number line.
Write the numbers where they belong or circle where they go.
6
15
9
+
=
+
=
-
=
-
=
30

1
.MD.
3
:
:
:
:
11:30
7:00
Draw hands on the analog clock.
©
2013
Corinna Woita
+
Teaching Fabulous Firsties
Write the time on the digital clock.

5
4
3
2
1
•
Which animal has
the
most
votes?
______________
•
Which animal has the
least
votes
?_______________
•
How
many votes does the
jellyfish have
?_________
•
How many more votes does the crab have than
the seahorse?
______
•
How many people voted in all?
______
•
How many votes do the crab and seahorse have
in all?
______
Use the graph below to answer the questions
.
Our
Favorite
Sea
Animals
4
.MD.
1
©
2013
Corinna Woita
+
Teaching Fabulous Firsties

Circle all the squares. Tell how you know.
_______________________________________
______________________________________
______________________________________
_
.G.
1
1
1
.G.
3
Draw lines to show how three
friends can equally share this candy.
.bar.
©
2013
Corinna Woita
+
Teaching Fabulous Firsties

What new shape can be made
from the triangles? Cut them out
and glue them together to form a
geometric shape.

56
47
Draw Base Ten blocks to represent each number
.
©
Corinna Woita
2013
+
Teaching Fabulous Firsties
1.NBT.2a
1
1
.NBT.1
=
_____
Count the Base 10 blocks and write the
number
number they represent.
1
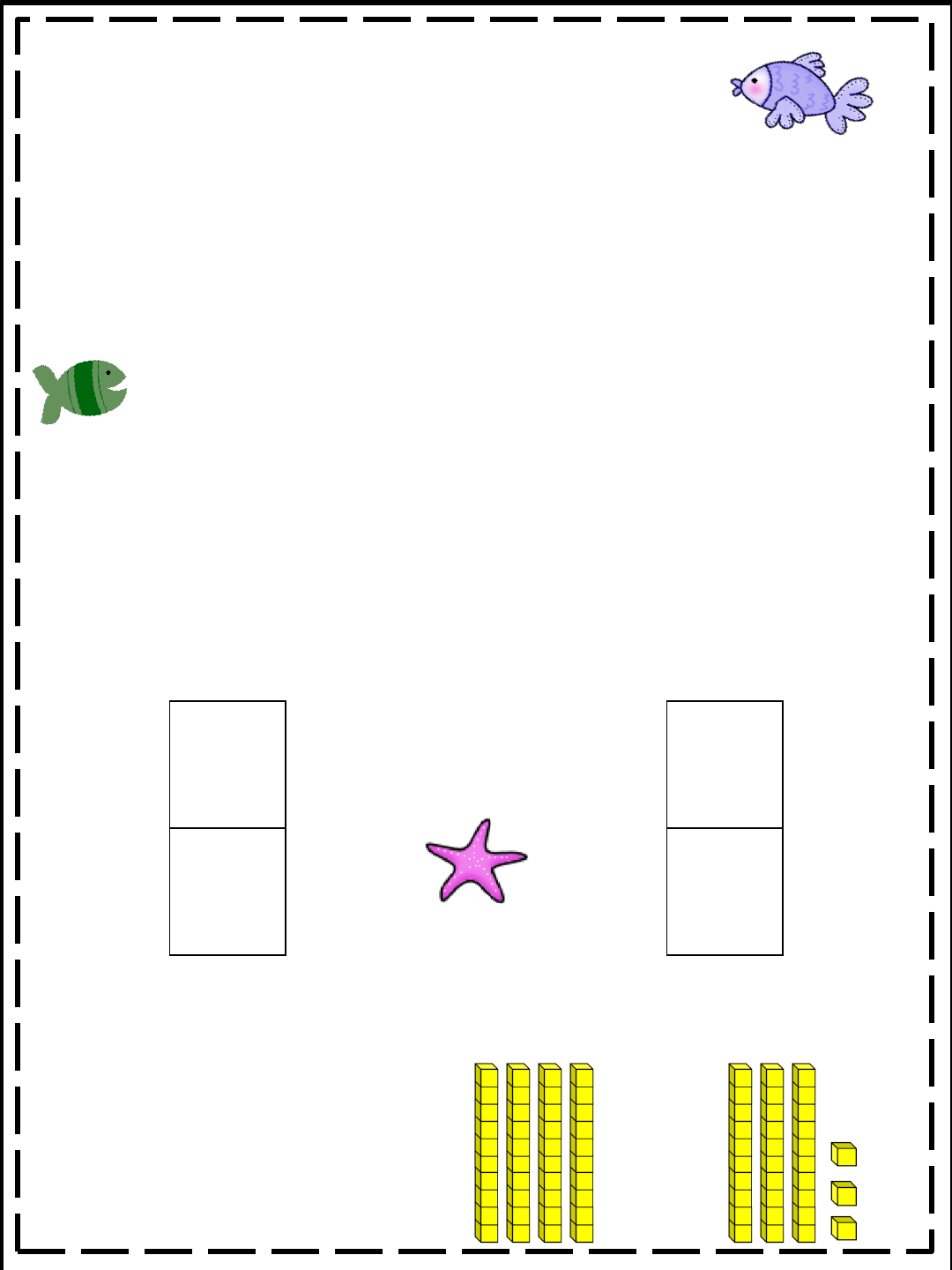
40+33=
___
+
©
Corinna Woita
2013
+
Teaching Fabulous Firsties
100
+
8
=
_____
100
+
6
=
_____
100
+
9
=
_____
Solve the problem.
1
.NBT.2b
.NBT.2c
1
Write the number of tens and ones.
=
76
__
tens &
__
ones
50
=
__
tens &
__
ones
47
48
15
51
Fill in the correct symbol.
= <
>
78
87
32
32
Solve the addition problem.
1
.NBT .
4
1
.NBT
.3

35
+21
83
-
50
27
-
13
43
+
_5
Solve the problem.
You
may draw base ten blocks to help you.
©
2013
Corinna Woita
+
Teaching Fabulous Firsties
.NBT .4
1

©
Corinna Woita
2013
+
Teaching Fabulous Firsties
34
57
Fill in the number grid with
10
more, 10 less, 1 more, and 1 less.
.NBT.5
1
1
.NBT.6
Solve the subtraction problem.
Draw an X on the Base 10 blocks you subtract.
45
-
10
68
-
24
