
UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022
UNCLASSIFIED
Headquarters USAREC Regulation 350-1
United States Army Recruiting Command
Fort Knox, Kentucky
Effective 19 September 2022
Training
Training and Leader Development
For the Commander:
MARK R. DANNER Official:
Colonel, GS
Chief of Staff
RONNIE L. CREECH
Assistant Chief of Staff
History: This publishes a revised USAREC Reg 350-1, which is effective 1 April 2024
Summary: Prescribes and consolidates policy and guidance for U.S. Army Recruiting Command training and leader development.
Applicability: To all military and civilian personnel assigned, attached, detailed, or on temporary duty with the U.S. Army Recruiting
Command.
Proponent and exception authority: The proponent of this regulation is the Commanding General, United States Army Recruiting
Command (USAREC). The proponent has the Authority to approve exceptions to this regulation that are consistent with controlling law
and regulations.
Army management control process: This regulation contains management control provisions in accordance with AR 11-2 but does
not identify key management controls that must be evaluated.
Supplementation: Supplementation of this regulation is prohibited.
Suggested improvements: Users are invited and comments and suggested improvements on DA form 2028 (Recommended Changes
to Publications and Blank Forms) directly to HQ USAREC, ATTN: RCSJA, 1307 3
rd
Avenue, Fort Knox, KY 40121-2725.
Distribution: This regulation is available in electronic media only.
UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 i
SUMMARY of CHANGE
UR Reg 350-1
Training and Leader Development.
This is an administrative revision, dated 1 April 2024
● Changed USAREC Risk Assessment and Counseling – Digital (URAC-D) to Leader Engagement Tool
(LET).
● Changed recruiting NCO to recruiter.
● Changed phase line to RSM
● Appendix J full re-write.

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 iii
Table List
3-1. Recruiting Courses, page 13
3-2. Order of Merit List-Sample, page 15
4-1. Mandatory Training, page 19
B-1. Sample of a completed USAREC Form 350-1.2, page 29
C-1. DTMS Color Codes for USAREC Training Events, page 32
F-1. Requisite Institutional or Organizational Courses, page 36
F-2. Trainer/Evaluator Assignments, page 37
G-1. Sample of a completed USAREC Form 350-1.4, page 45
I-1. Example USAREC Form 350-1.6 NPS CSTAR Part 1 – Operational Analysis, page 52
I-2. Example USAREC Form 350-1.6 NPS CSTAR Part 2 – Next Quarter Training Priorities, page 53
Summary Of Change

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 1
Chapter 1.
Introduction
1-1. Purpose
Establish policies and procedures for training and leader development within the U.S. Army Recruiting
Command (USAREC). Provide leaders with mandatory requirements, flexibility, and acceptable risk as it
pertains to training and leader development. Direct the preparation, implementation, documentation, and
disposition of all plans and programs associated with training and leader development.
1-2. References, forms, and Explanation of abbreviations
See Appendix A.
1-3. Associated publications
None listed
1-4. Responsibilities
Responsibilities are listed in section II of this chapter.
1-5. Records management (record keeping) requirements
The G-6 Administration Service Office is the POC for the Army Records Information Management
requirements.
1-6. Training challenge
The complexities of recruiting operations challenge commanders to develop the means and methods
necessary to train, develop, and sustain the recruiting force. Commanders will ensure soldiers and Civilians
are fully trained in their respective duty positions and mentored to provide professional development.
Training will focus on mission essential tasks and will encompass leaders, soldiers, and Civilians.
1-7. Training goals and objectives
Commanders will implement training that sustains and improves the performance of their units for short and
long- term mission capabilities. Commanders will invest in the individual leader and establish an environment
that promotes self-aware and adaptive leaders capable of responding to the ever-changing recruiting
environment.
1-8. Training management process
The training management process helps leaders identify training requirements and allows them to plan,
resource, execute, and evaluate training. Training management facilitates bottom-up feedback and top-down
guidance as outlined in FM 7-0 in order to create the most accurate representation of a unit’s readiness and
capabilities for commanders to implement their unit training programs. The routine completion of the
company/station training assessment review (CSTAR) by recruiting units assists commanders in assessing
their units and determines systemic training needs.
1-9. Training development process
The training development process begins when an actual or perceived performance deficiency is discovered,
this is called a triggering circumstance. Master trainers and training developers utilize the Analyze, Design,
Develop, Implement, and Evaluation (ADDIE) process and conduct in-depth needs analysis to assess
capabilities and performance gaps in any area of doctrine, organization, training, materiel, leadership and
education, personnel, facilities, and policy (DOTMLPF-P). Within USAREC the utilization of the CSTAR
guides the training development process and enhances the training management process. For utilization of
the CSTAR see Appendix J, USAREC TC 5-03.4, TRADOC Regulation 350-70, and TRADOC Pamphlet
350-70-1 provide guidance on the training development process.
1-10. Unit training
Commanders will develop, implement, and manage training at the unit level using Digital Training
Management System (DTMS). DTMS is the only authorized automated system for managing training in Army
units, assessing Individual tasks, and developing unit training plans and schedules IAW AR 350-1 (see
Appendices B and C).

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 2
1-11. Institutional training
USAREC manages training in schools for all soldiers and Civilian Staff (with the exception of
Noncommissioned Officer Professional Development System (NCOPDS), which the U.S. Army Human
Resources Command (HRC) manages. USAREC G3 Training Division manages the resident training base
and distributed courses through the Army Training Requirements and Resources System (ATRRS). Training
programs operate in accordance with the provisions of AR 350-1.
1-12. Evaluation of training programs
Commanders will establish training evaluation programs that compare the ability of individuals, leaders,
Civilians, and units to training standards. Evaluation is the basis for the commander’s unit training
assessment. To keep the training programs dynamic, leaders will use the AAR format located in DTMS to
determine the effectiveness of the training management cycle using:
Informal evaluations take place whenever a leader visits ongoing training. This type of evaluation
gives leaders a firsthand look at the training environment and the training’s effectiveness.
Formal evaluations (survey’s, testing, etc.) take place at scheduled times and are synchronized to
provide specific scope of a unit’s capabilities.
Internal evaluations measure the leader’s ability to train and the soldier’s and Civilian staff’s ability to
receive training as demonstrated through live-fire, role-play, and hands-on applications; these evaluations
put the evaluator at an advantage due to a pre-existing understanding of the Soldier’s and Civilian’s current
abilities and perceived potential.
External evaluations include the Organizational Inspection Program, brigade and USAREC staff
assistance visits, and inspector general inspections, the training assessment board (TAB), and training and
operational assessments (TOA).
1-13. Risk Management
Commanders are the risk management experts and ensure implementation of risk management occur in all
aspects of mission planning. Commanders will ensure that all military and civilian employees within their
command complete the online Risk Management Basic Course at https://safety.army.mil/ during in-
processing. Commanders will perform risk assessments in accordance with ATP 5-19, Risk Management.
Commanders will continually assess the risks in any training event to prevent loss of personnel and
equipment. All training involves some degree of risk, but commanders should not take unnecessary risks.
Commanders will assess their unit’s capabilities and evaluate risk when establishing training periods.
Commanders possess the flexibility to identify periods during the year when risk to mission is acceptable and
block out training periods that meet the unit, soldier, leader, and Civilian training needs. The CG, USAREC
provides a list of training topics where commanders can assume risk. While assuming risk is a leader’s
responsibility, it does not mean that training stops.
Chapter 2.
Responsibilities
2-1. Commanding General, USAREC
The Commanding General (CG), USAREC, exercises training and readiness oversight responsibilities by
developing training guidance; allocating the necessary resources to effectively implement training; evaluating
the conduct of training; providing subordinate commanders maximum time to train; and ensuring training is
managed using DTMS.
2-2. Command Sergeant Major, USAREC
The USAREC Command Sergeant Major is the Commanding General’s primary advisor for all training
matters. The USAREC CSM:
Administers USARECs Noncommissioned Officers Development Program (NCODP).
Responsible for the content and conduct of all USAREC Functional Courses and 79R NCOPDS.
Responsible for developing and conducting an annual USAREC CSM/SGM Course.
UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 3
Responsible for reviewing all NCOPDS cancellations and recommends actions to the USAREC
Deputy Commanding General (Operations).
Ensures USAREC and subordinate units maintain an order of merit list (OML) and soldiers prepare
academically and physically for professional development and functional courses.
Monitors USAREC's self-development training, Holistic Health and Fitness (H2F), and Army Combat
Fitness Test (ACFT) status.
Monitors all organizational training to include subordinate unit’s training plans.
Chairs all USAREC level promotion, selection, and award boards.
2-3. Assistant Chief of Staff G3
The ACS G3, through the Chief, G3 Training Division, publishes the annual training guidance, manages all
organizational training within USAREC, and ensures institutional training meets the demands of the
operational domain. Provides field training assistance and assessments to brigades and battalions, develops
training input to the quarterly training brief (QTB)/Operations Update Assessments (OUA), serves as
USAREC’s Schools, Quota Source, ATRRS, ALMS, and DTMS manager, develops and tests new training
products, and synchronizes training events with the USAREC long-range calendar. In conjunction with
Executive Services, the ACS plans and organizes the Annual Leaders Training Conference (ALTC).
2-4. Chief, G3 Training Division
Serves as the lead for all organizational training and ensures institutional training meets the
organizational/operational needs. G3 Training responsibilities include:
Authors USAREC Regulation 350-1 and the Annual Training and Leader Development Guidance.
Determines Senior Master and Master Trainer roles and responsibilities.
Assesses the deployment of Mobile Training Teams (MTT).
Serves as the USAREC Schools Manager and manages the scheduling of all functional and
institutional training.
Submits all Training Resources Arbitration Panel (TRAP) to HRC for additional training seat
requirements.
Serves as the USAREC Army Training Requirements and Resource System (ATRRS) administrator.
Serves as the USAREC Quota Source Manager.
Serves as the USAREC Army Learning Management System Blackboard (ALMS) Help Desk
Administrator.
Serves as the USAREC Digital Training Management System (DTMS) Administrator.
Serves as the USAREC Organizational Inspection Program (OIP) Coordinator.
Serves as the USAREC Master Resilience Trainer Coordinator.
Physically performs a minimum of 10 annual training and operational assessments to randomly
selected battalions. Authors a written summary following each assessment and an annual summary
comprising of all systemic training and operational trends from the FY.
Conducts a Quarterly Training Assessment Board (TAB) with all Senior Master Trainers to identify
training needs and share best practices.
Develops Training Support Packages (TSP) using distributed learning (DL), PowerPoint, and video to
support organizational training. Develops, coordinates, and conducts training for all new USAREC and Army
initiatives. (OPAT, Female Engagement Team, Lieutenant XO, etc.)
Reviews all training conducted, systemic training issues, and training requirements in order to develop
new training support packages or advise the change in current training guidance/programs.
Manages the USAREC 68W re-certification programs.

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 4
Manages the USAREC Leader Development Programs and Certifications:
Assistant Station Commander Program (ASCP).
Station Commander Certification.
Guidance Counselor/Operations NCO Certification.
Master Trainer Certification.
Company Leadership Certification.
Company Executive Officer Certification.
Battalion Executive Officer Certification.
Develops, coordinates, and conducts organizational training courses and programs:
Executive Officer Course.
Deputy Commanding General Semi-Annual Battalion Commander Training.
Recruiting Operations Officer Course.
CSM/SGM Training.
Governance Forum (Support)
Operations Training Course (Support)
Annual Leaders Training Conference (ALTC) in coordination with Executive Services.
Fusion Cell Training Program.
Maintains the USAREC G3 Training Repository SharePoint.
Maintains the USAREC Recruiter Tool Box.
2-5. Commandant Recruiting and Retention College (RRC)
The Commandant, Recruiting and Retention College provides 79R development and manages CMF 79
proponent requirements for USAREC. The commandant:
Manages all 79R/79S Institutional training.
Determines the RRC’s training capability to support USAREC’s projected out years student load and
serves as USAREC’s representative during the Annual Structure Manning Decision Review (SMDR).
Upon receipt from the USAREC Schools Manager, grants or disapproves exceptions to policy
requests for attendance to USAREC functional courses.
Conducts the Critical Site Selection Board (CTSSB), as required.
2-6. Commandant 79R/S NCOA
The Commandant, 79R/S NCOA serves as the proponent for 79R and 79S Senior Leader Course.
Directs operation of the NCO Academy.
Manages the 79R/S Noncommissioned Officer Professional Development Training.
Exercises command and control over all elements assigned or attached to the NCO Academy.
Effects coordination among elements of the NCO Academy and between the Academy, higher
headquarters, integrating stations, other schools, the installation, and external activities.
Supervises the deputy commandant.
Establishes missions and priorities for the NCO Academy.
Recommends UCMJ action over all assigned and attached personnel.

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 5
2-7. Brigade Commanders
Brigade commanders are responsible for training and will ensure training supports mission accomplishment,
professional and leader development, in addition to soldier and command guidance. Brigade commanders
will:
Provide training guidance and assistance to subordinate elements through the brigade operations
officer (S3).
Evaluate training conducted at battalion and company levels.
Publish quarterly training guidance.
Allocate resources necessary for training and mission accomplishment.
Assess subordinate units’ training guidance.
Deploys the Brigade Mobile Training Team as required to support organizational training needs.
2-8. Battalion Commanders
Battalion commanders the primary training managers in their units will ensure training supports mission
accomplishment, professional leader development, soldier and Family well-being, and adherence to
command guidance. Battalion commanders will:
Assess subordinate units’ training and adherence to the training guidance.
Develop, implement, and manage training.
Evaluate station training to ensure training is needs based, executed, resourced, and effective.
Publish quarterly training guidance.
Supervise and evaluate the sponsorship and reception and integration program.
Train, coach, and mentor company commanders.
Allocate necessary resources to support training at subordinate levels.
Supervise and validate all leader certification programs.
Deploy master trainers as required to support/assess organizational training needs.
Ensure the unit maintains soldiers certified to conduct Body Circumference measurements (BCM) /
height and weight. Soldiers conducting Body Circumference measurements must be trained/certified by
Master Fitness Trainer or Wellness personnel from a Military Treatment Facilities. Only certified soldiers
appointed on a Memorandum for Record are authorized to conduct official BCMs.
2-9. Brigade and Battalion Command Sergeants Major
The Brigade and Battalion Command Sergeants Major will:
Advise the commander on training priorities and oversee the delivery of all training.
Advise and mentor subordinate noncommissioned officers (NCO) regarding leadership and training
issues.
Manage the organization’s Noncommissioned Officer Development Program (NCODP), monitor self-
development training, and the unit’s ACFT status.
Manage the professional development of all 79R in their unit and assess potential candidates for
conversion to 79R.
Ensure their unit maintains an order of merit list (OML).
Supervise the implementation of their unit’s military schools program.
Ensure all soldiers are academically and physically prepared for professional development and
functional courses.
Review and participate in quarterly sustainment training.
UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 6
Brigade Command Sergeants Major serve as the primary trainer for their brigade’s Company Leader
Certification Programs. (See Appendix F)
Manages the effective use of their Master Trainers.
Advises on the planning of all major training events.
2-10. Executive Officers
Brigade and Battalion Executive Officers manage the staff to accomplish the commanders’ intent. The XO:
Validates the task proficiency of all staff members IAW the position description and Training and
Evaluation Outlines (T&EO).
Serves as the lead for Fusion Cell Operations and trains the staff to synchronize efforts.
2-11. S3s
Brigade and battalion S3s manage all training functions and ensure training follows the commander’s training
guidance. S3s:
Ensure adequate resourcing of training activities.
Assess subordinate unit’s training guidance.
Review and consolidate subordinate units’ training schedules through DTMS.
Review erroneous enlistment and liaison reports and provide preventive and corrective guidance
counselor (GC) training.
Monitor the execution of the schools OML.
Monitor mandatory and organizational needs-based training activities and events.
Enforce the utilization of CSTARs and compliance with the standards outlined within this regulation.
Supervise station commander quarterly leader development (SCQLD) planning.
Prepare QTB/Operations Update Assessment presentations.
Maintain the training calendar.
Monitor leader certification programs.
Senior rate the Senior Master Trainer.
2-12. Operations Sergeants Major
The brigade and battalion operations sergeants major advises the battalion commander, CSM, and S3 on
Army recruiting operations. Operations SGMs:
Advises the commander on training trends, priorities, and monitors unit training.
Advises the S3 on training shortfalls and senior master trainer (SMT) activities.
Advises and mentors subordinate NCOs regarding leadership and training issues.
Advises the commander and CSM on systemic trends found through CSTARs.
Advises the commander and CSM on self-development training statistics, ACFT, and operational
proficiency.
Propose locations to deploy Master Trainers and determines the objectives of the Mobile Training
Team, if required.
Ensure the unit maintains an OML and validate the academic and physical qualifications of soldiers
prior attending PME and functional courses.
Validate leader certification program compliance.
Rate the Senior Master Trainer.

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 7
2-13. USAREC, brigade, and battalion master trainers
Senior master trainers (SMT) and master trainers (MT) are the command’s primary training managers and
responsible for assessing, developing, implementing, conducting, and managing training at USAREC,
brigade, and battalion levels.
Note: SMTs are supervisors and assign MTs responsibilities using the following guidelines:
USAREC Senior Master Trainer (SMT) and Master Trainers (MT):
Enforces the standards outlined in this regulation.
Ensures all training is loaded within the Master Event Calendar found on the G3 SharePoint.
Serves as the command’s training subject matter expert.
Helps determine brigade and battalion training needs.
Coordinates training programs.
Conducts Training and Operational Assessments (TOA).
Serves as liaison between USAREC and the RRC for the integration of new technologies and training
priorities.
Coordinates and conducts the quarterly USAREC Training Assessment Board (TAB).
Conducts training at USAREC-level training functions.
Facilitates bottom-up feedback from lower echelons across the command in order to identify
systemic training issues, new training requirements, or training opportunities.
Analyzes training data provided by brigades and provide recommendations for inclusion in the
command's training plan and guidance.
Maintains the Recruiter Toolbox.
Must complete Black Board level 101, or higher, certification.
Must complete Common Faculty Development Instructor Course (CFD-IC).
Serves as primary or assistant system administrator for DTMS (see Appendix C).
Serves as training developer and content subject matter expert for all USAREC distributed learning.
Serves as the manager for the Assistant Station Commander Program (ASCP)
Assists the Recruiting and Retention College with Training Development needs.
Serves as USAREC’s Schools Manager.
Monitors all USAREC organizational and institutional training.
Develops and manages all leader development and leader certification programs.
Serves as USAREC’s Army Training Requirements and Resource System (ATRRS) manager.
Serves as USAREC’s Army Learning Management System (ALMS) administrator.
Serves as USAREC’s Blackboard manager.
Manages oversight on the Master Trainer Roster located on the USAREC G3 Training SharePoint.
Serves as the Quota Source Manager. In coordination with USAREC G1 and G8-Force
Management determines projected out year strength requirements. Compares requirements against SMDR
projections and submits to the RRC for training load capabilities and subsequent changes to the SMDR.
Brigade Senior Master Trainers (SMTs) and Master Trainers (MTs):
Enforces the standards outlined in this regulation.
Ensures all training is loaded within the Master Event Calendar found on the G3 SharePoint.

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 8
Serve as the Mobile Training Team.
Manage and evaluate brigade training program.
Manage brigade schools program.
Obtain and maintain ATRRS access.
Maintain an OML.
Verify enrollment in ALMS or Blackboard for the DL pre-resident phase of the Station Commander
Course (SCC) and Health Care Recruiter Course (HCRC)
Facilitate the scheduling of officers and enlisted soldiers for functional courses at the Recruiting
Retention College (RRC).
Submit all battalion request for NCOPDS school, course deferment, cancellation, or changes via the
IPPSA – Personal Action Request to the USAREC Schools Management IPPSA User List.
Submit all battalion request for Functional school, course deferment, cancellation, or changes via
the USAREC G3 Schools Management SharePoint.
Submit exception to policy (ETP) requests via the USAREC Schools Management SharePoint. All
ETPs will route through the USAREC Schools Manager. The USAREC Schools Manager will route the ETP
through the approval channels and schedule the soldier in ATTRS.
Serve as the primary or assistant system administrator for Digital Training Management System
(DTMS) (see Appendix C).
Coordinate brigade level boards and training events.
Must complete Black Board level 101 certification.
Must complete Common Faculty Development Instructor Course (CFD-IC).
Review and validate completion of the Assistant Station Commander Program for Soldiers
requesting conversion to 79R.
Track brigade level incentive/awards program.
Monitor all leader certification programs.
Enroll soldiers in the Company Leader Certification Program on the G3 Training SharePoint and
maintain their record until certified.
Review CSTARs in order to identify systemic training needs.
Lead the brigade’s portion of the quarterly USAREC Training Assessment Board (TAB).
Manages oversight of the Master Trainer Roster for the entire BDE located on the USAREC G3
Training SharePoint, ensure all BDE Trainers are accurate on the Roster.
Ensure Battalions stay current on all required Mandatory training IAW AR 350-1.
Battalion Senior Master Trainers SMTs and Master Trainers:
Enforces the standards outlined in this regulation.
Ensures all training is loaded within the Master Event Calendar found on the G3 SharePoint.
Manage and evaluate battalion training program.
Review Company and Station Training Assessment Review (CSTAR) and identify systemic trends to
bring to the attention of the Operations Sergeant Major.
Review and assist Company Command Teams in developing a company training plan.
Initiate USAREC Form 350-1.4 (Reception and Integration Checklist) for all new Recruiters reporting
to the organization.
Enroll soldiers into applicable Leader Development Programs

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 9
Initiate the applicable Leader Development Program when warranted for the Soldier per this
regulation.
Monitor and track all Leader Development Programs for the organization in the Leader Development
SharePoint (see Appendix J).
Monitor and track the administration and conduct of certification programs (see Appendix F)
Provide training assistance for all Leader Development and certification programs.
Review and closeout the ATP, CLP, and Certification Programs, only when the records are
complete. Forward discrepancies or inadequate documentation to the Battalion CSM upon identification.
Manage battalion schools’ program, actively review the organization to identify soldiers needing
schools.
Obtain and maintain ATRRS access.
Maintain an OML when needed for schools.
Facilitate the scheduling of soldiers to attend resident NCOPDS through the brigade senior master
trainer via the IPPSA – Personal Action Request (PAR).
Verify enrollment in ALMS or Blackboard for the DL pre-resident phase of the Station Commander
Course (SCC) and Health Care Recruiter Course (HCRC)
Facilitate the scheduling of officers and enlisted soldiers for functional courses at the Recruiting
Retention College (RRC) utilizing the USAREC G3 Schools Management SharePoint.
Submit all battalion request for NCOPDS school/course deferment, cancellation, or changes to the
brigade school’s manager via the IPPSA – Personal Action Requests.
Submit all battalion request for Functional school/course deferment, cancellation, or changes to the
brigade school’s manager via the USAREC G3 Schools Management SharePoint.
Serve as the primary or assistant system administrator for Digital Training Management System
(DTMS).
Administer, track, and upload into DTMS all ACFT results and height/weight stats for the Army Body
Composition Program IAW AR 350-1.
Deploy MTs throughout the battalion as needed to conduct training.
Coordinate all battalion level boards and training events.
Submit School Request on all newly reclassified NCOs to CMF 79R to attend Station Commander
Course within 30-days of reclassification.
Manages oversight on the Master Trainer Roster for the BN located on the USAREC G3 Training
SharePoint, ensure all BN Trainers are accurate on the Roster.
Monitor and track all required Mandatory training IAW AR 350-1.
2-14. Company Commanders
Company commanders are responsible for all sustainment and professional development training for their
company. Company commanders will:
Review external training guidance.
Protect and enforce the execution of station training.
Conduct training assessments.
Maintain station’s readiness through the routine utilization of UF 1-201.1 (Recruiting Inspection Log).
Develop, implement, and manage the company’s training plan utilizing the Company/Station Training
Assessment Review (USAREC Form 350-1.6 (See Appendix I).
Review, validate, and approve the Station Training Plans.

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 10
Monitor soldiers’ ability to attend professional schools to include reviewing suspension of favorable
actions report (FLAG) IAW 600-8-2.
Manage the company’s Future soldier Training Program.
Evaluate collective and individual training conducted at station and Recruiter levels.
Ensure the Advanced Training Program, Station Commander Certification, and Noncommissioned
Officer Leader Development Program (NCOLDP) are properly conducted and maintained (see Appendix F
and Appendix J).
Ensure soldiers are receiving sustainment training as necessary.
Provide or request resources necessary for training.
Monitor station physical fitness programs.
Manage the company’s ACFT program.
Participate in the battalion’s targeting board.
Develop the company’s Recruiting Operations Plan, to include annual training guidance, within 90-
days of the fiscal year, approved by battalion commander, and validated by brigade commander.
2-15. First Sergeants
First Sergeants are the company training experts and primary trainers of station commanders. First
Sergeants will:
Advise the commander on training priorities, assist in the identification of training needs, and direct
and monitor delivery of all training.
Enforce the execution of station training.
Conduct training assessments and conduct the quarterly review of all stations and the company’s
CSTARs.
Review external training guidance.
Assist and monitor the company’s self-development and Holistic Health and Fitness (H2F) training.
Monitor the NCOPD and ATP and evaluate Recruiter’s progress throughout the program’s (see
Appendix D and Appendix J).
Manage the company’s NCODP.
Ensure soldiers prepare academically and physically for professional development and functional
courses.
Monitor and perform training roles with the Station Commander Certification and enforce training with
the Assistant Station Commander Program. (See Appendix F).
Support the Distributed Leader Courses (DLC) and Guided Self-Development (GSD) programs.
Train and counsel, the company’s station commanders.
Counsel prospective Department of the Army (DA) select soldiers on conversion potential and training.
Identify training and operational gaps through daily In-Progress Reviews (IPR) with station
commanders.
Manage the training of all newly converted MOS 79R within the company.
2-16. Medical Recruiting Station Officer in Charge (OIC)
Medical Recruiting Station OIC, in collaboration with the Station Commander, will provide analysis and
assessment for completion of the CSTAR.
As Army Medical Department subject matter experts (SME), Station OIC will contribute to training and
development of Recruiters in the conduct of recruiting operations.

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 11
Conduct weekly AAR.
Develop HCR Station Operation Plan.
Establish population health care Recruiting environment.
2-17. Station Commanders
Station Commanders are the primary trainers in their stations and responsible to provide soldiers with
training that enables recruiting success, professional and leader development, and adherence to command
guidance. Station commanders will:
Develop, implement, and manage the station’s training plan utilizing the Company/Station Training
Assessment Review (CSTAR) (See Appendix I).
Provide collective and individual training.
Properly implement and execute NCOPD and the Advanced Training Program’s (see Appendix D and
Appendix J).
Ensure soldiers receive sustainment training opportunities within their PMOS as necessary and
provide necessary training resources (Example: 68W NREMT recertification or other MOS requirements
outlined in DA PAM 611-21).
Conduct Noncommissioned Officer Development Program (NCODP) as an extension of the 1SG
NCODP.
Identify training and operational gaps through daily In-Progress Reviews (IPR) with Recruiters.
Chapter 3.
Institutional Training and Education
3-1. Description
USAREC’s institutional training at the Recruiting and Retention College (RRC), supported by distributed
learning (DL) resources, provides soldiers, leaders, and Civilians the knowledge and skills necessary to
operate successfully in the recruiting environment. Resources include specialty training, training
development, DL, and training support products.
3-2. Command policy
The professional development of officers, NCOs, and Department of the Army (DA) Civilians is vitally
important to the command. The command will afford all personnel the opportunity to attend professional
development courses and accumulate continuing education units required to maintain and recertify their
branch and military occupational specialty (MOS) credentials.
Within the guidelines prescribed below, all officers, NCOs, and Civilians will attend required courses
applicable to their position and grade. See table 3-1 for a complete list of Recruiting and Retention College
courses.
USAREC staff responsibilities:
The USAREC CSM will monitor course compliance and periodically brief the CG regarding all NCO
courses.
Chief, G3 Training Division, will:
(a) Ensure equitable distribution of training seats.
(b) Provide USAREC CG and CSM updates on course attendance, to include no-shows, low fills, and
any other inconsistencies within the USAREC school system.
(c) Coordinate with Human Resources Command (HRC) for scheduling 79R and 79S NCOPDS.
(d) Request a Training Requirements Arbitration Panel (TRAP) when training seat requirements
change.
Brigade and battalion commanders and CSMs will:
UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 12
(a) Monitor attendance rates for all PME and functional courses from their organizations.
(b) Certify that soldiers are academically and physically capable of attending PME and functional
courses.
(c) Provide replacements from their respective OMLs if soldiers are not prepared to attend.
(d) Commanders will take appropriate administrative action to eliminate no-shows and reduce soldier
cancellations.
(e) Commanders will review temporary profiles in accordance with the prerequisites for course
attendance.
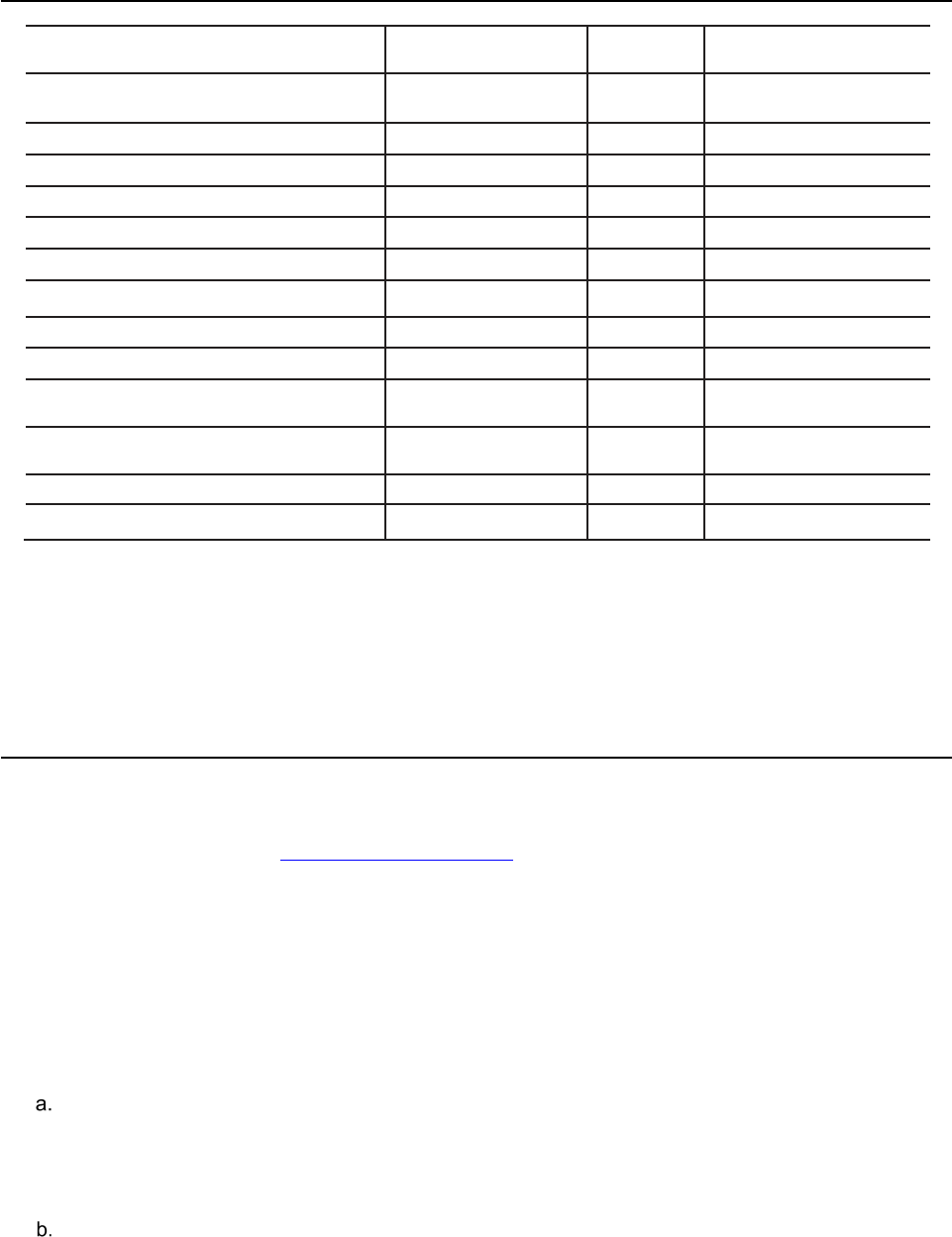
UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 13
Table 3-1. Recruiting Courses
Notes:
1. SCC requires completion of pre-resident phase 1 DL in Blackboard.
2. Prerequisites include Phase I consisting of 15 working days of hands-on training (10 days
at the Military Entrance Processing Station (MEPS) and 5 days in a battalion operations
shop) (waiverable).
3. Commanders and First Sergeants will be school trained prior to taking command.
Exception to policy (for officers) must be approved by USAREC, CG.
4. Selection for attendance to 79R/79S SLC requires completion of DLC3.
3-3. Course information
Access information pertaining to Army schools and courses through the Army Training Requirements and
Resources System (ATRRS) at https://www.atrrs.army.mil/
ATRRS is the Army’s management information
system for managing student input to training including any required DL courses. This automated support
tool establishes training requirements, determines training programs, manages class schedules, allocates
class quotas, reserves training seats, and records student attendance.
3-4. Order of Merit List (OML)
An OML determines the most qualified personnel to attend NCOPDS, specialty, functional and professional
development courses. All battalions will maintain an OML and submit it to the brigade SMT each month. The
brigade SMT will compile a consolidated OML and scrub it for accuracy monthly.
Note: A sample OML is at Table 3-2.
USAREC determines the order and selection for 79R functional course attendance. HRC determines
the order and selection for attendance for NCOPDS, but it remains the battalion’s responsibility to track
soldier’s eligibility and NCOPDS requirements. NCOPDS notifications are sent via ATRRS directly to the
soldier with a courtesy copy to the soldier’s First Sergeant and CSM. Upon receipt of notification, the soldier
will inform their immediate supervisor.
Senior Master Trainers will immediately notify the next soldier on the OML to replace cancellations or
deferments. This best prepares the soldier and avoids losing a training seat. HRC manages replacements for
all NCOPDS, USAREC only actions requests for NCOPDS and cannot schedule or directly cancel NCOPDS.
Cancellations, deferments, and train ahead requests are routed through G3 Training Schools Manager to the
Course
Name
Resident Location
and Duration
Prerequisite Remarks
Army Recruiter Course (ARC)
Fort Knox / 6 weeks, 4
days
No
Valid CAC (Common Access
Card)
Health Care Recruiting Course (HCRC)
Fort Knox / 3 weeks
No
Guidance Counselor/Operations Course (GCOC)
Fort Knox / 4 weeks
Yes
See Note 2
Station Commander Course (SCC)
Fort Knox / 4 weeks
Yes
See Note 1
Master Trainer Course (MTC)
Fort Knox / 2 weeks
No
Company Executive Officer Course (COXOC)
Fort Knox / 2 weeks
No
Recruiting CO CDR/ 1SG Course (RCCFSC)
Fort Knox / 3 weeks
No
See Note
3
Recruiting Pre-Command Course (PCC)
Fort Knox / 2 week
No
Recruiting Senior Leader Course (SLC)
Fort Knox / 3 weeks
Yes
See Note 4
Retention Senior Leader Course (SLC)
Fort Knox / 4 weeks
Yes
See Note
4
Career Counselor Course
Fort Knox / 8 weeks 2
days
No
Transition NCO Course
Fort Knox / 2 weeks
No
Common Faculty Development Instructor Course
Fort Knox / 2 week
No

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 14
USAREC CSM and DCG but are actioned after approval by HRC exclusively.
Commanders will remove a soldier from the OML for the following reasons:
Unfavorable personnel actions in accordance with AR 600-8-2.
Temporary medical profiles that prevent attendance of courses in accordance with AR 40-501 and
AR 350-1.
Valid personal situations and situations outlined within AR 614-200 Chapter 5.
Bar to continued service IAW AR 601-280.
Declination of continued service IAW AR 601-280.
Soldiers with a course assignment will complete TRADOC Form 350-18-2-R-E (The Army School
System (TASS) Unit Pre-Execution Checklist) prior to departing for school. TRADOC Regulation 350-18
details completion of the form. Soldiers must present TRADOC Form 350-18-2-R-E during course in
processing.
The minimum entries on an OML are as follows:
Name of course (for example, SCC).
Name of officer, NCO, or Civilian.
Unit, organization, activity, or RSID.
Start date of course (if scheduled).
End date of course (if scheduled).
Phase I completion date (if applicable).
SMTs will validate that height and weight occur at the same time as diagnostic ACFT and potential
students are within regulatory compliance. Update all records, to include DTMS, whether the individual
meets the height and weight standards or the body fat composition percentage.
TRADOC Form 350-18-2-R-E completion date.
Date orders received and remarks (as applicable).

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 15
Table 3-2. Order of Merit List-Sample
COURSE
NAME/UNIT RAN
K
START END
PH I
1
HT/WT
P/F
BF
2
ACF
T
P/F
DATE
3
PRE-EX
4
ORDERS REMARKS
SCC
Burns, P
5D1C
SFC
7/23/18
8/17/18
6/19/18
74/200
P
297
P
7/18/18
7/18/18
SCC
James, A
5B2A
SSG
9/18/17
10/12/17
9/4/17
SCC
Lawrence, E
5D2W
SFC
GCOC
Mathew
E 5C3T
SFC
9/4/17
9/1/17
71/174
P
300
P
8/21/17
GCOC
Edward D
5C2G
SFC
HCRC
Andrew B
5Z4Z
SSG
HCRC
Grey, T
5B1T
SFC
RCCFSC
Brow M.
5D8
CPT
7/10/18
7/27/18
5
61/117
P
267
P
6/21/18
6/21/10
RCCFSC
Carlson B.
5D1
CPT
8/14/18
8/31/18
72/188
P
234
P
6/21/18
ROOC
Black, J
5D
CPT
10/2/17
10/20/17
9/13/17
ALC
Henderson, D
5C1F
SGT
10/2/17
10/27/17
8/10/17
SLC
White, R
5F3
SFC
7/3/10
8/4/10
66/160
P
270
P
5/11/17
SLC
Baker C
5D
SFC
9/24/17
10/26/1
7
8/4/17
SLC
Roberts T
5B2A
SSG
11/13/17
9/22/17
Notes:
1. Date of completion of Phase I training.
2. Enter body fat percentage when soldier exceeds weight standards of AR 600-9.
3. Date soldier took the ACFT or scheduled to take it.
4. Date pre-execution checklist completed in accordance with TRADOC Regulation 350-18.
3-5. Resident course deferments/cancellations
Three reasons for resident course deferments or cancellations exist: Compassionate, medical, or
operational. Leaders will adhere to the following deferment/cancellation procedures.
Compassionate deferments must meet the reassignment criteria outlined in AR 614-200 Chapter 5.
Request medical deferments in accordance with AR 350-1.
Requests for an operational deferment is an exception to policy requiring approval by the first
General Officer (GO) in the chain of command.
Note: (NCOPDS) takes precedence over USAREC functional courses.
All functional course deferment or cancellation request must be submitted by the Brigade SMT/MT to
the USAREC Schools Managers via the “Schools Management” link on the G3 Training SharePoint
homepage, NLT 30 days prior to the class start date. Requests must include:
DA Form 4187 signed by Company, Battalion and Brigade Commanders. The name listed in the
commander block will match what is on the Common Access Card (CAC) signature block.
All NCOPDS course deferment or cancellation request must be submitted using an IPPSA – Personal
Action Request (PAR) submitted by the Brigade SMT/MT to USAREC Schools Managers IPPSA User List.
Requests must include:
PAR routed through and signed by Company, Battalion and Brigade Commanders.

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 16
BDE commander memo.
BN Commander memo.
STP.
DA Form 705 or a DA Form 705 from DTMS verified and signed by the soldier’s company
commander.
DA Form 5500/5501 (if required).
DA Form 1059 required if attending a NCOPD and was released from course.
DA Form 4856 required for HT/WT failure or academic failure and any other documentation (as
required).
Commanders and Command Sergeants Major are responsible for:
Ensuring the Brigade Commander and Brigade Command Sergeant Major are aware of NCOPDS
deferments or cancellations prior to submission.
Interviewing all previously deferred soldiers to determine merit and justification for submitting a HQDA
G3 exception for rescheduling.
Interviewing any soldier who previously received a negative DA Form 1059 from any course prior to
submitting an exception for rescheduling for that same course.
3-6. Army Recruiter Course (ARC)
The ARC teaches Recruiter candidates the interpersonal, conceptual, administrative, technical, and tactical
skills necessary to succeed in the contemporary recruiting environment. The curriculum provides training in
the principles of adaptive leadership, eligibility, technology systems, interpersonal communications, Army
programs, time management, prospecting, interviewing, and processing. The ARC is open to active duty and
Army Reserve enlisted soldiers in the rank of sergeant and above, contractors, and DA Civilians that meet
screening criteria IAW USAREC and HRC policies.
Note: Former Recruiters that return to USAREC after 12-months absence must re-attend the ARC.
3-7. Health Care Recruiter Course (HCRC)
The HCRC provides specialized training for health care Recruiter/Officers (HCRs). Course curriculum
addresses product knowledge, interview skills, basic eligibility, and the processing procedures necessary to
perform as an HCR.
The HCRC is available to officers, NCOs, and Civilians selected for duty as HCRs. The course is a 3-
week resident course that addresses the interview techniques and communication skills necessary to interact
with health care professionals and commission them as Army Medical Department officers. The course uses
conceptual, analytical, and procedural applications in all aspects of training.
3-8. Station Commander Course (SCC)
Graduates of the SCC are awarded ASI V6 and able to manage station assets, employ system
resources, evaluate, and train Recruiters, and execute and guide recruiting operations.
Attendance at the SCC is mandatory for all soldiers prior to assuming a station commander position.
The SCC is a 4-week resident course taught at the RRC.
3-9. Company Executive Officer Course (COXOC)
The COXOC teaches Company Executive Officers the conceptual, foundational, administrative, technical,
and tactical skills necessary to successfully perform the roles of a company XO. The COXOC is open to first
lieutenant (1LT) active duty officers that meet screening criteria for assignment IAW USAREC and HRC
policies.
3-10. Guidance Counselor Operations Course (GCOC)

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 17
The GCOC provides the training necessary to perform in the positions of a guidance counselor (GC),
operations NCO, USAREC liaison, and HQ USAREC G3 staff. Soldiers in MOS 79R, contractors, and DA
Civilians are eligible to attend the course. Soldiers must be in the rank of staff sergeant through master
sergeant.
Phase I is the nonresident portion, supervised by the senior guidance counselor (SGC) and/or
operations noncommissioned officer in charge (NCOIC). Phase I includes 15 working days of hands-on
training (10 days at the military entrance processing station (MEPS) and 5 days in the battalion or brigade
operations shop). Phase I must be completed prior to reporting for the resident phase. The battalion SMT is
responsible for confirming completion of the pre-resident packet and checklist certification.
Phase II is the resident portion of the course and is 4 weeks in length. The GCOC is divided into four
major areas of concentration.
Delayed Entry Program and Delayed Training Program enlistment procedures.
GC administrative functions.
Delayed Entry Program and Delayed Training Program status procedures.
Battalion operations functions. Personnel must graduate from the GCOC to remain eligible for
assignment to the duty position. Upon graduation, students are awarded the additional skill identifier V7.
3-11. Master Trainer Course (MTC)
The Master Trainer Course (MTC) provides training for all NCOs with duty as a senior master trainer and
master trainer. The 2-week course at Fort Knox focuses on training senior master trainers and master
trainers how to effectively assess recruiting teams, evaluate CSTARs, evaluate the application and
development of needs based training, manage training though DTMS and ALMS, manage a schools
program, and utilize the assess, develop, design, implement, and evaluate (ADDIE) process, and plan and
execute large training events.
3-12. Recruiting Company Commander/First Sergeant Course (RCCFSC)
All incoming company commanders, master sergeants, and high potential for promotion (HPFP)
sergeants first class, designated to assume command of a recruiting company commander or first sergeant
position will attend the integrated RCCFSC prior to command or position. Master sergeants and HPFP
sergeants first class are placed on the brigade OML by the brigade SMT and scheduled to attend the
RCCFSC once the soldier is slated for a first sergeant position. Company Commanders are scheduled by
HRC, Officers branch prior to assignment to USAREC. If the commander does not attend prior to
assignment, they will attend within 90 days of reporting.
The curriculum addresses recruiting doctrine, policies, programs, procedures, and adaptive
leadership. The course includes instruction, practical exercises, and experience-based training to assist new
company commanders and first sergeants in planning recruiting operations.
Company commanders must successfully complete the 3-week resident course taught at the RRC to
be enrolled in the Company Leader Certification Program to become certified and earn the Army Basic
Recruiting Badge.
It is USAREC’s policy to send newly assigned company commanders on temporary duty (TDY) to the
3-week resident phase in route to their new assignment. Company commanders receive 10 to 14 days of
overlap time in their new assignment to complete the Leader Transition Program (see Appendix H).
Note: The CG, USAREC, may approve officer requests to report directly to their new assignment prior to
attending the RCCFSC. If this occurs, the Company Commander must attend the course within 90 days of
reporting. If they do not attend, they will need a justification MFR from their battalion commander.
3-13. Recruiting Pre-Command Course (RPCC)
The RPCC provides training for newly assigned brigade and battalion commanders and all non-79R
command sergeants major selected through the command selection process. The curriculum addresses
recruiting doctrine, policies, programs, procedures, adaptive leadership, command responsibilities, recruiting
integrity, and recruiting command culture.

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 18
The RPCC consists of a 2-week resident course at the RRC, Fort Knox, KY. Currently assigned
brigade and battalion commanders serve as instructors and mentors throughout the course. Practical
examples enhance the student learning experience.
The Leader Staff Orientation (Para 4-7) and the Deputy Commanding General’s Semi-Annual,
Battalion Commander Training (Para 4-9) support the tenets of PCC.
3-14. Civilian development
The Army training vision is to support total force readiness and mission accomplishment by providing and
empowering commanders and managers with the authority necessary to accomplish the training and
development of a technically competent, high-performing, civilian workforce. Civilians help the military
accomplish its missions in several ways. First, civilian employees may have technical skills that are critical
and in short supply in the uniformed service. The Civilian Corps provides continuity and support to the
recruiting force. Therefore, it is critical to invest in Civilian development. Commanders, supervisors, and
managers share responsibility for enabling Army Civilian employees to reach their full potential (see
Appendices H and I).
Chapter 4.
Training in Units and Organizations
4-1. Climate and leadership
Leaders must understand how their units recruit using the full range of recruiting functions and
operations. They must know how to plan, execute, and assess individual and collective training. All training
must be innovative, doctrinally sound, and reinforce mission-essential, collective, and individual recruiting
tasks.
Commanders will develop training programs to improve and sustain proficiency in mission-essential
tasks. The chain of command is responsible for the training and performance of subordinates and trainers
within their organizations. Commanders develop and publish short-range, mid-range, and long-range training
guidance in accordance with FM 7-0. The commander’s training guidance establishes the unit’s training
program and guides subordinate unit-training programs. Unit-training programs will:
Provide soldier and Civilian critical skill training in accordance with Training & Evaluation Outlines
(T&EO) located in the Central Army Registry (CAR), the Army Training Network (ATN) and the USAREC G3
Training SharePoint.
Provide required training resources.
Develop and execute training plans that provide quality training and result in proficient individuals,
leaders, and units.
Commanders will manage available training resources, implement cost effective techniques, and
keep in mind that every training requirement and expenditure contributes directly to accomplishing the
recruiting mission.
4-2. Mandatory training.
Integrate mandatory training into normal training processes using alternative training formats
appropriate to the topic throughout the year. Mandatory training will be conducted IAW the USAREC Annual
Training Guidance.
See AR 350-1 for Army mandatory training tasks outlined in table F-1 (located on the Army Training
Network [ATN])
In addition to Army mandatory training requirements, USAREC mandates the annual completion of
Family Advocacy Program (FAP) training.
Table 4-1 displays the USAREC mandatory training events. Commanders may require completion of
other training tasks as a result of unit assessments.

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 19
Table 4-1. Mandatory Training
Notes:
• Station training, in addition to regular individual needs-based training, will be conducted weekly as a
result of CSTAR input.
• Company commanders will conduct company training quarterly. Training is conducted in accordance
with CSTAR results and annual training guidance.
• First sergeants will conduct station commander training monthly. Training is conducted in
accordance with the commander’s operational assessment and NCOPD. First sergeants will conduct
individual training with station commanders during battlefield circulations.
• Commanders will conduct company commander, first sergeant, and battalion staff training annually.
Staff Training may consist of Fusion Cell operations. Duration depends on needs, budget, and
conference packet requirements.
• Battalion commanders will conduct an ATC. All soldiers will attend, and training and content will be in
accordance with the USAREC Lines of Efforts, this regulation, and the USAREC Annual Training
Guidance (operations order).
• Battalion commanders will conduct SCQLD. Required attendees are the battalion CSM, all company
commanders, first sergeants, and station commanders.
• Brigade commanders will conduct QTBs. required attendees are the brigade CSM, battalion
commanders and CSM, and company commanders and first sergeants.
• Battalion Commanders will develop and conduct Quarterly AGR Training.
4-3. Organizational Courses and Programs
Organizational courses and programs fill training gaps between institutional training and operational/leader
requirements, sustains critical skills, and validate core competencies. USAREC conducts several courses to
build and enhance the skill, knowledge, and attributes of the force.
4-4. Advanced Training Program (ATP)
The ATP is the first operational domain training requirement for recent ARC graduates upon arrival to the
recruiting station. This program trains foundational skills and focuses on Prospecting, Interviewing,
Processing and Future Soldier Management. The 150-day program begins immediately following arrival to
the organization. The ATP requires station commanders to train Recruiters on foundational skills and provide
the Recruiter with a “Trained” status. The soldier has 150-days to receive a “Trained” status on all skills. (See
Appendix J).
SUBJECT Annual Semi-
annual
Quarterly
Monthly
Weekly
Remarks
Company training
X
Note 2
Station Training
x
Note 1
Station Commander training
X
Note 3
Co Cdr. 1SG, battalion staff training
X
Note 4
Annual Training Conference (ATC)
X
Note 5
Station
Commander Quarterly Leader Development
(SCQLD)
X
Note 6
AGR Training
X
Note 8
Operations Update Assessment (OUA)
X
Quarterly Training Brief (QTB)
X
Note 7
Brigade quarterly training program
X
See Appendix F

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 20
4-5. Assistant Station Commander Program (ASCP)
The Assistant Station Commander Program (ASCP) is a quarterly distributed, self-enrollment, distance
learning program designed to establish leadership and recruiting foundation skills for NCOs assuming the
role of Assistant Station Commander. This course also serves as the first step in the reclassification process
to 79R. This course broadens the scope of the recruiter’s technical and tactical knowledge, leadership,
education, and duty responsibilities.
4-6. Battalion XO Course
The XO Course outlines the recruiting process and provides the techniques and procedures
necessary to manage and coordinate a battalion and/or brigade staff. This is a five-day resident course at
HQ USAREC.
Executive Officers may request an additional three-day recruiting staff development/fusion cell MTT
for their respective staff. The MTT is conducted at the Battalion HQs with a minimum of the primary Fusion
Cell members; XO, S3, S2, A&PA, ESS, VRS, and Social Media Manager (If applicable). Using an actual
objective from the Battalion Commander, the staff works through the Military Decision Making Process
(MDMP) and develops a COA brief that can be actioned. The end state is to establish staff synchronization
using the proper methodology to support the commander’s intent.
4-7. Leader’s Staff Orientation (LSO)
The Leader Staff Orientation (LSO) is an extension program to the USAREC Pre-Command Course. Brigade
Commanders will schedule and lead up to a five-day orientation for new battalion commanders and non-79R
CSMs. The orientation’s content is decided by the Brigade Commander. The orientation must occur within 90
days following the new battalion commanders/non-79R CSM’s completion of the Recruiting Pre-Command
Course and an AAR must be submitted in DTMS NLT 5 days following completion of the LSO.
4-8. Battalion Recruiting Operations Officer Course (BROOC)
The BROOC is a 3-week Distributed Learning (dL) organizational course that provides training for all newly
assigned recruiting operations officers. The curriculum includes: enlistment processing, eligibility, incentives,
prospecting, missioning, and how to evaluate mission progress using data analysis. This course is a
prerequisite for enrollment into the Battalion S-3 Officer Certification program.
4-9. Company Executive Officer Course (COXOC)
The COXOC is a 3-week Distributed Learning (dL) institutional course that provides training for all newly
assigned company executive officers. The curriculum includes: recruiting standards, intelligence and market
analysis, enlistment eligibility, interviewing, planning, leader development, developing networks, sustainment,
missioning, and how to evaluate mission progress using data analysis. This course is a prerequisite for
enrollment into the Company Executive Officer Certification program.
4-10. Company Recruiting Operations Officer Course (CROOC).
The CROOC is a 3-week Distributed Learning (dL) organizational course that provides training for all newly
assigned company recruiting operations officers. The curriculum includes: recruiting standards, intelligence
and market analysis, enlistment eligibility, interviewing, planning, leader development, developing networks,
sustainment, missioning, and how to evaluate mission progress using data analysis. This course is a
prerequisite for enrollment into the Company Recruiting Officer Certification program.
4-11. Deputy Commanding General (DCG) Semi-Annual Battalion Commander Training
The Deputy Commanding General Semi-Annual Battalion Commander Training is a two-to-three-day session
for battalion commanders during their first 6-months in position. Each brigade commander will select a senior
battalion commander to serve as a mentor and participant during the training. The USAREC DCG facilitates
the training with the intent of sharing ideas and best practices, generating cross talk, and preparing
commanders to identify and counter common pitfalls.
4-12. Command/Operations Sergeant Major Course
The CSM/Operations Sergeant Major Course is an organizational course hosted by the USAREC CSM or G3
Sergeant Major depending on attendees. Attendees may consist of CSMs or Operations SGM, or both
depending on current operational and training needs. Content will be needs based and or to reintegrate the

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 21
graduating class of 79Rs from the United States Sergeants Major Academy and prepare them to assume
responsibilities as an operations sergeant major. The course will be led by subject matter experts.
4-13. Certification Programs
Leaders at every level will invest in the training and development of their subordinates. Performing
sustainment training and validating the competencies of soldiers and leaders, and staff. The following are the
positions requiring certification.
Station Commander
Company Executive Officer/Recuriting Operations Officer
First Sergeant
Company Commander
Brigade/Battalion S-3
Senior Guidance Counselor
Senior/Master Trainer
Operations NCO
Brigade/Battalion Executive Officer
Soldiers are required to complete their applicable certification at least once. Certification includes
assessing common and duty position knowledge, leadership, and professional competencies commensurate
with their rank and position. Brigade Commanders maintain the discretion to remove soldiers from position
for failing to recertify. Battalion Commander may require a soldier to reenroll in the certification program.
(See Appendix F).
4-14. Records of military and civilian training
Commanders and station commanders will maintain training records through DTMS to assist them in the
development of their unit training programs. Sign in rosters will be uploaded into DTMS and AARs completed
upon completing training events. Individual training conducted outside of scheduled training will be annotated
on UF 350-1.2 (Training Record) and maintained in that soldier’s counseling record. Units will plan, schedule,
and post training in DTMS. Additionally, near-term training plans will be posted in company and station areas
on UF 350-1.1 (Near Term Training Plan). In accordance with AR 350-1 Chapter 5-2d. (3) DTMS is the only
authorized automated system for managing, recording training, and establishing unit assessments.
4-15. Leader Professional Development (LPD)
Leaders are technically and tactically competent, practice self-discipline, self-awareness, and
successfully adapt to an ever-changing operational environment. Commanders are responsible for leader
professional development programs in their units and for providing a learning climate where leaders:
Value subordinate input.
Communicate, listen, and care.
Establish and maintain candor and open dialogue at all levels.
Develop units that possess a sense of trust and share responsibilities.
Have the freedom to exercise initiative where honest mistakes are forgiven and from which lessons
are learned.
Have an active role modeling as coaches, counselors, and mentors.
Execute relevant, challenging, and complex education and training.
Deliberately plan and leverage opportunities for unit/organizational assignments and extra duties to
challenge and provide new experiences for leaders.
Demand and provide honest developmental feedback to guide self-awareness and development.
Formulate professional development around the Army Leadership Requirements Model.

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 22
Employ the fundamentals of developing leaders: setting conditions, providing feedback, enhancing
learning, and creating opportunities.
Allow time for subordinates to pursue educational and self-developmental opportunities.
Develop leaders to operate effectively at their next level of responsibility and ensure preparation for
success at their next level of education.
The commander’s primary responsibility is to ensure that their unit can perform its mission.
Accordingly, the commander focuses training activities on mission performance including Officer
Professional Development (OPD) and Noncommissioned Officer Professional Development (NCOPD) and
developing a broad set of professional competencies.
A key component of LPD is the Leader Transition Program. The program gives new leaders an
opportunity to accompany departing leaders through their operational area prior to the change of command
or transfer of authority/responsibility. The program provides an excellent opportunity for training and
mentoring incoming leaders. Appendix H provides detailed information on this program.
For more guidance on leader development reference FM 6-22.
4-16. Officer Professional Development (OPD)
Commanders will design an OPD to foster a common bond, broaden the knowledge base of
subordinate officers, and conduct quarterly OPD sessions on topics related to professional and personal
growth.
Refer to DA Pam 600-3, the Army’s professional development guide for officers, for branch functional
area, and key position information.
4-17. Noncommissioned Officer Professional Development (NCOPD)
The unit’s NCOPD will center on the environmental and behavioral requirements of recruiting and will
support the commander’s LPD program. The NCOPD will focus on building the warrior spirit and contributing
to the professional and personal growth of NCOs. A strong NCO support channel is the key to accomplishing
all unit missions effectively. Commanders will enforce and CSM/1SGs will execute NCOPD.
As with all LPD, the NCOPD is a command responsibility. The program reflects command priorities
and experiences for LPD with management by the CSM or unit’s senior noncommissioned officer.
Leaders will refer to DA Pam 600-25, which is the Army’s NCO professional development guide for
career management field (CMF) information.
Leaders will refer to TC 7-22.7 to frame and goal NCOPD around the Noncommissioned Officer
Common Core Competencies (NCOC3).
4-18. Unit training events
In some cases, events may occur through nontraditional means to minimize training costs (TEAMS,
teleconferences, Blackboard, ALMS DL training modules, etc.). Likewise, units may reduce costs by
conducting training at military installation facilities, National Guard armories, and USAR centers.
Commanders at each level will determine training requirements and select the best method to conduct
training. Department of the Army and TRADOC guidance contains specific criteria, limitations, and
responsibilities pertaining to training events. Commanders will comply with all training event guidance IAW
the USAREC’s Annual OPORD pertaining to Training and Leader Development and USAREC Conference
Policy.
USAREC training events:
Annual Leaders Training Conference (ALTC) at USAREC HQs designated location.
Governance Forums (Semi-annual)
Operations Update Assessments (OUAs) x 2
Other G-staff conferences may occur with CG approval and if funds are available.
Brigade training events:

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 23
Off-site training conducted once each year - The list of participants is at the discretion of the brigade
commander.
Annual Operations Conference.
Quarterly Training Briefs (QTB) x 4 - Participants include, brigade command group, battalion
commanders and CSM, Company Commander, First Sergeant, and supporting brigade staff.
Note: Commanders may conduct a QTB virtually to meet budget constraints.
Unit Training Management Course x 1 - Participants include brigade and battalion SMTs and MTs.
Operations Conference x 1 - Participants include brigade and battalion operations officers and
noncommissioned officers in charge.
S2 conference x 1 - Participants include brigade and battalion S2 officers.
Fusion Cell Training Conference x 1 - Synchronized with Executive officers, A&PAs, ESSs, S3s, and
the S2.
Battalion training events:
One off-site. Participants include battalion commander and CSM, company commanders and first
sergeants, and battalion staff principals.
Station Commander Quarterly Leader Development (SCQLD). Sessions x 4; participants include
battalion commanders and CSM, company commanders, first sergeants, and station commanders.
Annual Training Conference (ATC) following the USAREC ALTC.
AGR Recruiter and Army Reserve Recruiting training. Sessions x 4; participants include battalion
commanders and CSM, AGR Operations NCO, all AGR Recruiters.
4-19. Specialized training assistance
Specialized training assistance is available for brigades and battalions through the USAREC G3, Training
Division. Specialized training assistance teams focus on leadership, staff, and recruiting operations systems.
Commanders will forward requests for USAREC or outside agency support through the Brigade to USAREC
G3, Training Division.
4-20. Self-Development
Self-development is a life-long learning practice. In support of the Army Learning Development Strategy
(ALDS), three types of self-development exist to develop leaders professionally and personally. They are:
Distributed Learning Content (DLC), Guided Self-Development and Personal Self-Development.
Commanders and leaders at all levels will mentor and influence their subordinates to perform self-
development. Commanders will ensure all eligible NCOs are enrolled in their applicable level of DLC and will
ensure soldiers complete their level within 180 days of enrollment. Leaders will assist all soldiers and Civilian
Staff to incorporate guided and personal self-development into Individual Development Plans (IDP) in the
Army Career Tracker (ACT)

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 24
Appendix-A
References
Section I
Required Publications
Army publications are available on the Army Publishing Directorate website available at
https://armypubs.army.mil/
AR 40-501
Standards of Medical Fitness
AR 350-1
Army Training and Leader Development
AR 350-10
Management of Army Individual Training Requirements and Resources
AR 600-8-2
Suspension of Favorable Personnel Actions (Flags)
AR 600-8-8
The Total Army Sponsorship Program
AR 600-9
The Army Body Composition Program
AR 601-1
Assignment of Enlisted Personnel to the U.S. Army Recruiting Command
AR 601-280
Army Retention Program
AR 614-200
Enlisted Assignments and Utilization Management
DA Pam 600-3
Commissioned Officer Professional Development and Career Management
DA Pam 600-25
Army Noncommissioned Officer Professional Development Guide
ADP 7-0
Training
TRADOC Regulation 350-18
The Army School System
USAREC Regulation 601-210
Enlistment, Accessions, and Processing Procedures
UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 25
Section II
Related Publications
AR 600-8-22
Military Awards
AR 600-8-24
Officer Transfers and Discharges
AR 600-20
Army Command Policy
AR 635-200
Active Duty Enlisted Administrative Separations
DA Pam 350-58
Army Leader Development Program
DA Pam 611-21
Military Occupational Classification and Structure
ADP 6-22
Army Leadership and the Profession
FM 7-0
Training
FM 6-22
Leader Development
TC 7-22.7
The Army Noncommissioned Officer Guide
FM 7-22
Holistic Health and Fitness (H2F)
USAREC TC 5-03.4
Training and Leader Development
ATP 5-19
Risk Management
Section III Prescribed Forms
USAREC Form 350-1.1
Near-Term Training Plan (Prescribed in para 4-12)
USAREC Form 350-1.2
Training Record (Prescribed in para 4-12)
USAREC Form 350-1.4
Reception and Integration checklist (Prescribed in Appendix H-2a.)
USAREC Form 350-1.6
NPS Company/Station Training Assessment Review (CSTAR) (Prescribed in para. 2-14c.)
UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 26
USAREC Form 350-1.8
AAR – Right Seat/Left Seat Ride (Prescribed in Appendix H-2b. (2))
USAREC Form 350-1.9
New Recruiting NCO Board Score Card (Appendix K)
USAREC Form 350-1.10
Leader Transition Program (Appendix H)
Section IV Referenced Forms
DA Form 4856
Developmental Counseling Form
DA Form 705
Army Physical Fitness Scorecard
DA Form 5500
Body Fat Content Worksheet (MALE)
DA Form 5501
Body Fat Content Worksheet (FEMALE)
TRADOC Form 350-18-2-R-E
The Army School System (TASS) Unit Pre-Execution Checklist

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 27
Appendix-B
Training Management and Records
Section I.
Training Plans
B-1. Long-range planning
USAREC will post its annual training and leader development guidance to DTMS allowing a
minimum of 90 days planning time for subordinate echelons to establish their training plans and training
guidance (Appendix C). The command training guidance (CTG) is posted to the organization’s long-range
training calendar in DTMS. The CTG is a reference for the planning, preparation, execution, and evaluation
of training throughout the long-range planning period. Examples of topics normally addressed in the CTG
are:
Commander training philosophy.
Major training events.
Leader training.
Recruiting staff development training.
Individual training.
Self-development.
Training evaluation and feedback.
New equipment training.
Resource allocations.
Training management.
Risk management.
Commanders post the long-range planning calendar concurrently with their CTG and post it into
DTMS. The calendar graphically depicts the schedule of events described in the CTG. Once approved by
higher headquarters, long-range planning calendars are “locked in” to provide planning stability for
subordinate organizations. Only the approving commander can change a long-range planning calendar.
Upload Annual/Command Training guidance in DTMS in the Training, Plan, and Document Library
folder. Include the FY into the title of the document.
B-2. Short-range planning. Short-range planning and subsequent plans cover a specific quarter within the
fiscal year and perfect the long- range training strategy and is the commander’s responsibility.
Brigade and Battalion Commanders’ will submit short-range training plans (Quarterly Training
Guidance) to the next higher-level headquarters for\approval and post in DTMS NLT 6-weeks prior to the
execution date of the plan.
Company Commanders and Station Commanders (NPS) will complete the Company Station
Assessment Review (CSTAR) in Appendix J and develop their next Quarter training plan NLT 5 working
days following the end of last RSM of the Quarter, submitted to the next higher level for approval, and
uploaded into DTMS.
Medical Recruiting Brigade conducts a CSTAR every 60-days and will develop the next Quarter
training plan within five (5) calendar days following distribution of data from Brigade.
Short-range planning should be flexible and allow for modification or revision based on individual unit
needs. It will enable the commander to accomplish the following:
Translate training requirements from the annual training plan into a logical series of training events.

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 28
Provide detailed guidance to trainers, including training objectives.
Coordinate resources allocated to support designated training events.
All Training guidance and CSTAR will be uploaded in DTMS in the Training Plan and Document
Library folder. Include the QTR and FY into the title of the document.
Note: Station CSTAR are uploaded into Company document library. Company CSTAR are uploaded into the
Battalion document library.
B-3. Near-term planning
The near-term training adjustments covers a one-month period within the short-range (Quarter) training plan
and completed by the company commander with input from the first sergeant and station commanders.
Near-term training plans further refine the short–range plan and focuses on immediate training needs that
arise or not covered in the short- range training plan. Leaders will make adjustments in the training plan
within DTMS. The near-term plan is designed to:
Make final coordination for the allocation of resources for training.
Ensure training objectives specified in the short-range training plan are scheduled and executed.
Prepare detailed training schedules and lesson plans in a timely manner.
Section II
Training Records
B-4. DTMS Individual Training Record
Individual Training Records (ITR) within DTMS are sufficient records of training regarding performance.
Commanders will enforce accurate input of training completed, to include GO/NO-GO status of individual
tasks within DTMS. Training subjects outside of the individual tasks found within the applicable Soldiers
Manual for Training Guidance will be created as local tasks in order to record training on that subject. Local
tasks must include accurate and objective actions, conditions, and standards during their creation in order to
provide and accurate assessment of the soldier’s performance against those actions, conditions, and
standards when training on that local task.
B-5. Event Sign-in Rosters
Sign-in rosters for scheduled training events are sufficient records for training conducted. Event rosters will
be created in events scheduled in DTMS and printed for signatures of trainees to prove attendance. Sign-in
rosters will be uploaded into events in DTMS after the event is concluded. In the event that a sign-in roster
cannot be completed the commander will document participation through a memorandum that can be
uploaded into that training event in DTMS.
B-6. Event Counseling (DA Form 4856)
Specific instances of superior and substandard performance in training must be annotated on a
developmental counseling form (DA Form 4856). Event counseling sessions are utilized in conjunction with
training in order to guide soldiers in identifying strengths and also weakness in order to capitalize on those
strengths and overcome weaknesses. These instances of developmental counseling must outline a plan for
the counseled soldier moving forward that clearly depicts current performance and performance milestones
to strive towards.
B-7. USAREC Form 350-1.2
All individual training is recorded on USAREC Form 350-1.2 (Figure B-1) located in the USAREC
Publications Library. Trainers must place special emphasis on the “Trainee’s response and/or comments”
regarding the training they received. The trainee’s feedback will validate the training’s effectiveness and
assist in the planning of future training. There is no requirement to upload USAREC Form 350-1.2 into a
soldiers ITR. Copies will be maintained in the trainee’s counseling folder.

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 29
Table B-1. Sample of a completed USAREC Form 350-1.2

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 30
Appendix-C
Digital Training Management System
General
The Digital Training Management System (DTMS), located at https://dtms.army.mil, is a web-based
planning and management tool that facilitates an organization’s ability to plan, resource, and track
individual and collective training. DTMS also provides access to Army standard training products. DTMS is
the only authorized automated system for managing, recording training, and establishing unit assessments
for Army units. DTMS is mandatory for the management, planning, and recording of all soldiers, leader,
and Civilian training.
DTMS is an unclassified, sensitive system. Treat all information as For Official Use Only (FOUO).
Leaders and system administrators will ensure users do not enter classified data into the system.
C-2. Responsibilities
USAREC G3, Training Division, is the proponent for DTMS in USAREC. The G3 will appoint a
primary and assistant system administrator, which are typically the USAREC SMT and a USAREC MT.
The system administrators will:
Act as liaison between USAREC, higher headquarters, subordinate units, and the Combined Arms
Center \ DTMS program manager.
Manage the access plan as specified in paragraph C-5.
Ensure users are trained on the application and assist subordinate commands to train their first
sergeants, and station commanders.
Manage user accounts for soldiers assigned to subordinate units.
Represent USAREC on the DTMS Requirements Control Board working group in accordance with
the Army’s charter.
Brigade commanders will appoint a primary and assistant system administrator. System administrators
are typically the SMT and MT. System administrators will:
Act as liaison between their command and USAREC’s system administrator.
Train subordinate units on the application.
Ensure subordinate units are training leaders and operators how to use the application.
Manage user accounts for their command in accordance with the access plan outlined in paragraph
C-5.
Refer to the G3 Training Standard Operating Procedures and the current Annual Training Guidance
for further guidance.
Battalion commanders will appoint, on appointment orders, a primary and assistant DTMS
administrator. System administrators are typically the SMT and MT. System administrators will:
Act as liaison with higher headquarters.
Train users.
Manage user accounts in accordance with the access plan outlined in paragraph C-5.
Refer to the G3 Training Standard Operating Procedures and the current Annual Training Guidance
for further guidance.
Company Commanders are responsible for ensuring subordinates are entering training plans and
training results into DTMS.
Commanders will use T&EOs, with T/T-/P/P-/U ratings, to continuously assess unit performance,
whether during training or actual operations, to identify reasons for performance success and shortfalls.

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 31
T&EO assessments will be recorded in DTMS.
Refer to the G3 Training Standard Operating Procedures and the current Annual Training Guidance
for further guidance.
Annotate outcomes/certifications according to the guidance below.
Training Schedules will include:
(a) Sergeant’s time training
(b) Certification training
(c) Administrative Actions
(d) Mandatory Training
(e) Annual Training
C-3. Training
System administrators at all levels are responsible for training on DTMS within their commands. The
USAREC G3, Training Division, is the primary DTMS administrator and trainer.
USAREC G3 Training DTMS system administrators will maintain training materials on the USAREC
G3 Training SharePoint that is applicable to all access levels.
Brigade and battalion commanders will ensure all SMTs and MTs are trained on DTMS. Commanders
are responsible to ensure all subordinate units maintain DTMS operators.
Commanders will ensure all training events are planned and scheduled. Tasks that are associated
with each training event will be logged in DTMS in order to ensure soldiers receive credit for the training.
Manage training as required in this regulation, the current USAREC Fiscal Year OPORD, Annual
Training Guidance, G3 Training SOP, AR 350-1, ADP 7-0, and FM 7-0.
C-4. Troubleshooting and support
DTMS support is available from system administrators; however, users are highly encouraged to
first access the “Help” menu on the DTMS Homepage
https://atn.amy.mil/unit-training-management-
(DTMS knowledge base). DTMS FAQs address most assistance issues and solutions. The DTMS
Knowledge Base allows users to submit questions and issues to the DTMS Help Desk. Prior to submitting
a request, users will first explore both the user’s manual and previous postings on the Knowledge Base.
DTMS issues that are not specific to the application will be addressed the chain of command and not
to the DTMS Knowledge Base. The DTMS Knowledge Base will not resolve USAREC specific issues.
G3 Training Division serves as USAREC’s help desk and can assist with most technical and USAREC
specific issues with DTMS.
C-5. DTMS management
Brigades will provide a list of their current DTMS Managers to the USAREC DTMS Manager on 01
April and 01 October (Or, first working day following) of every fiscal year in order to facilitate tracking of
DTMS training capability throughout the Command.
Commanders may permit or deny access to anyone within their command with the exception of the
system administrators. Group roles are designated roles related to the user’s position. Individual roles cannot
be removed from the groups, but additional individual roles can be given to those not already part of the
group.
Commanders, along with the system administrators, will identify additional trainers who require
access. Commanders will ensure that system administrators:
Quarterly: Review all personnel that have access to DTMS for accuracy and completeness.
Deactivate DTMS access for users no longer assigned or no longer serving in DTMS manager roles.

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 32
Deactivate DTMS access for users who have not accessed DTMS in 365 days. This report can be
generated via the User Reports function of DTMS.
System administrators have the authority to deny access to anyone who violates this regulation, other
directives, or fails to fulfill their responsibilities. If a system administrator denies anyone access, they must
immediately report the action to their supervisor, commander, and system administrator at the next level of
command.
C-6. DTMS
Commanders will review their administrative processes and reduce the burden on units and soldiers as well
as make recommendations to eliminate or simplify tasks through their chain of command.
There is no requirement to scan and upload supporting documents into DTMS in order to validate
the Commander’s input of training, either collective or individual. However, the individual training record
(ITR) will contain the:
Date and score (if applicable) for completion of common mandatory training requirements in
accordance with established regulations.
Completion of other requirements as approved and directed by the Command and published in
appropriate USAREC publications.
Completion information from diplomas, certificates of training (DA Form 87) including ALMS course
completions, weapons qualification scorecards, physical fitness test scorecards (DA Form 705),
height/weight and body composition worksheet (DA Form 5500 and DA Form 5501), and driver/operator
training qualifications.
Leaders at the lowest echelon will input soldier permanent and temporary profiles in DTMS ensuring
that limitations are annotated and available date for record ACFT are properly listed. No personal medical
data, to include cause of injury, will be input in to the DTMS.
Calendars: All units will manage their training calendars using the Unit Training Plan (long-range
calendar and Training Management Calendar (short-range calendar) functions (see Appendix B).
METL: USAREC does not have an Army approved METL.
The Company/Station Training Assessment Review (CSTAR) from both the company and each recruiting
station will be uploaded in the Document Library. Station CSTAR will be uploaded into the Company Library
and Company CSTAR in the Battalion Library under the Training > Plan > Document Library in DTMS.
Refer to Table C-1 for proper color coding for all events.
Event Type Event Color Examples of Events
TAB
Boards
OUA/QTB
Team Building Exercises
AR 350-1 / UR 350-1 Tasks
Unit Command Directed
Training Stand Down
Assessments
IG
RSD
OIP
Any other command led inspections
Purple Station Training Events
Teal Company Training Events
Green Battalion Training Events
Grey Brigade Training Events
Collective Tasks
Universal Collective Tasks listed in
CAR/METL/CATS
Local Collective Tasks
Collective tasks indivative of Recruiting
Command only
Holidays
Listed in Annual Training Guidance
Training Holidays
Training Holidays
Inspections
Red
Unit Training
Olive
Maroon
Admin
Blue
Mandatory Training
Yellow

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 33
Appendix-D
79R Noncommissioned Officer Leader Development Program
D-1. General
The Noncommissioned Officer Leader Development Programs contain the tenets of the Army Leader
Development Strategy and Leader Development Model. It incorporates the unique USAREC training
requirements to support and strengthen the Corps while preparing NCOs for current and future mission
capabilities regardless of assignment. All leaders will support, invest in, and execute this program.
Note: A USAREC proponent review may alter the proponent and school requirements.
Figure D-1. Sample of the 79R Leader Development Program

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 34
Appendix-E
Self-Development Domain
E-1. General
The Self-Development Domain is where planned and goal-oriented learning reinforces and expands the
depth and breadth of a leader’s knowledge base, self-awareness, and situational awareness. Self-
development bridges learning gaps between the operational and institutional domains and sets conditions for
continuous learning and growth. Leaders at all levels will complete, influence, and assist subordinates in
becoming life-long learners using the three self- development techniques. Responsibilities for:
All leaders:
Promote the self-development of all individuals in USAREC.
Provide resources and training to enrich the self-development within USAREC.
Battalion/brigade commanders/command sergeants major ensure that in addition to unit training
outlined in this regulation that soldiers are afforded time to self-develop.
Company commanders and first sergeants:
Guide and resource the self-development of 79R based off personnel development community found
on the Army Career Tracker and the 79R professional development model.
Counsel Recruiters on the utilization of DA PAM 611-21 MOS qualifications in order to remain
qualified in their PMOS.
Station commanders will guide and resource the self-development of Recruiters based off their unique
PMOS and individual goals.
Recruiters are responsible for remaining informed on changes in their PMOS in regard to
qualifications, certifications, systems, and professional/personnel development models in addition to self-
developing in recruiting skills.
E-2. Army Career Tracker (ACT)
The Army Career Tracker (ACT) is a single aggregated source for assignment history, experience, skills,
education, civilian acquired skills, interests, and extended relationships. As a leader development tool, it
integrates data on training, education, and experiential learning from a number of source systems into one
personalized and easy to use interface, provides users a more efficient and effective way to monitor their
career development, allows supervisors to track and advise employees on their leadership development and
career program managers the ability to reach the geographically dispersed careerists. In USAREC leaders
are faced with developing and guiding the self-development of soldiers from a variety of PMOS. The ACT
enables leaders to assess themselves, their careers, and the same for their subordinates regardless of
geographic dispersion. Each Career Management Field (CMF) has a personnel development community
where leaders and soldiers can find information and resources to guide self-development and establish clear
career goals based on individual CMF and broader leader development.
E-3. Guided Self-development (GSD)
Guided Self-development (GSD) is recommended, but optional learning to help prepare leaders for changing
technical, functional, and leadership responsibilities throughout their career. A critical GSD component is the
use of boards. Leaders should prepare for and participate in boards, such as NCO of the
Month/Quarter/Year and the Sergeant Audie Murphy/Sergeant Morales Clubs, to broaden their knowledge
base, instill discipline, and to improve communication skills and leadership potential.
E-4. Army E-Learning (SkillSoft)
Army E-Learning is a free resource for soldiers to access professional reading material, tutorials,
certifications, and courses for information technology skills, well-being, business skills, productivity &
collaboration tools, engineering, and much more. Army E-Learning includes a library of free professional
books that can assist in professional self-development and that can be used to assist in GSD.

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 35
E-5. Educational Activities
The Army’s goal is for every soldier to become a warrior learner continuously learning and growing in their
tactical, technical, and civilian education domains. Many self-development activities come from programs
and services offered through the Army Continuing Education System (ACES). The ACES assists soldiers
with self- development as described in DA PAM 600-25. The ACT site is also an incredible resource for the
individual soldier to view all available resources the Army has under the “my planner/career map” tab.
E-6. Functional Academic Skills Training (FAST)
FAST offers instruction in reading, mathematics, and communication skills to help soldiers function on the
job, prepare for advanced training, and meet prerequisites for continued education.
E-7. Earning a College Degree
All NCOs should have a goal of earning their degree while assigned to USAREC. College level courses are
available through installation education centers that coordinate with participating colleges to provide on-post
programs that lead to award of an associates, bachelors, and/or master’s degree.
E-8. Army Correspondence Course Program (ACCP)
The ACCP provides a variety of self-study correspondence courses that are specific to each MOS and CMF.
Leadership and training management courses are available, which gear towards professional development.
Proponent schools develop the courses, many of which consist of sub courses that provide soldiers
promotion points upon completion.
E-9. Knowledge Skills, and Abilities
Development of self-awareness in various human domains; recognizing self-awareness as a vital
aspect of leader development and psychological health in the USAREC environment. There are a number
of psychological factors that influence one’s success as a leader. A central factor is an accurate awareness
of one’s competency and areas for growth, also known as self-awareness. Self-awareness is acquired
through an internal self-assessment and/or input from external sources like peers, training, coaching, or
other experiences in life of a personal or professional nature. However, in the absence of integrating
personal experiences and/or systemic feedback humans tend to be very poor at self-awareness and are
not prone to critical self-assessments. Self-awareness empowers leaders to develop emotional
intelligence, which is necessary for long-term effectiveness in personal and professional endeavors.
The critical knowledge, skills, and behaviors (KSB) involved in the development of healthy self-
awareness consist of:
Adaptive Leadership
Emotional Intelligence
Cognitive Flexibility
Perspective Taking
Communication Skills
Behavioral Performance Science/Mental Toughness
Courage, Commitment, and Humility

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 36
Appendix-F
Certification Programs
F-1. General
The purpose of the USAREC Certification Programs is to validate training, knowledge, and the
capabilities to perform in the assigned position and to sustain skill sets. All station commanders, first
sergeants, company commanders, company executive officers, senior/guidance counselors, operations
NCOs, battalion S3 officers, battalion executive officers, and senior/master trainers will participate in the
certification program.
Brigade commanders maintain the authority to:
Remove a soldier from position for failing to certify.
Authorize Certification Exam Retests or for the soldier to repeat the certification program.
Administration:
USAREC certification programs consist of the following requirements.
(a) Assignment to the position and to be a graduate of the requisite Institutional or Organizational
course. (See Table F-1.)
Table F-1. Requisite Institutional or Organizational Courses
POSITION
COURSE
*Recruiter (See Appendix J)
Army Recruiter Course -I
Assistant Station Commander
Assistant Station Commander Program-O
Station Commander
Station Commander Course -I
Senior/Guidance Counselor/Operations NCO
Guidance Counselor Operations Course -I
Senior/Master Trainer
Master Trainer Course -I
Company Recruiting Operations Officer
Company Recruiting Operations Officer Course - DL
Company Executive Officer
Company Executive Officer Course -DL
Company Commander/First Sergeant
Company Commander/First Sergeant Course -I
Brigade to Battalion S3 Officer
Recruiting Operations Officer Course-DL
Brigade to Battalion Executive Officer
Executive Officer Course -O
O=Organizational, I=Institutional, DL=Distant Learning, *=Separate policies for Recruiters see Appendix J
(b) Attend/participate in and complete either the brigade quarterly training programs (Company
Commanders and First Sergeants) such as the Outrider Program, Warrior University, Victory University, etc.,
within 90-120 days of assignment or graduation of the RCCFSC whichever is later.
(c) Trained/evaluated by the assigned evaluator within 90-180 days of assignment and graduation from
an Institutional or Organizational course, whichever is later.
(d) Achieve an 80% or higher on the position certification exam following completion of the Brigade
Academy or receive a “Trained” evaluation on all required tasks by the select evaluator.
Commanders may add additional tasks to the certification program or centralize training through
venues such as the Station Commander Quarterly Leader Development (SCQLD), etc.
Responsibilities:
Figure F2 displays the primary (P) and or alternate (A) trainer/evaluator assignments.

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 37
Table F-2. Trainer/Evaluator Assignments
Commanders/Command Sergeants Major: Enforce, validate the quality, timeliness, and completion of
all certification programs.
Trainers/Evaluators will:
(a) Train/evaluate IAW Training and Evaluation Outlines (T&EO) located in the USAREC Leader
Development Program SharePoint.
(b) Record evaluations in the USAREC Leader Development Program SharePoint.
Senior Master/Master Trainers will:
(a) Enroll soldiers in the certification program.
(b) Monitor the status of candidates and provide monthly updates to the Commander and CSM.
(c) Complete the administrative requirements to request enrollment in the Blackboard Certification
Exam.
F-2. Station Commander Certification Tasks
Station Commanders must certify in 15 tasks.
The enrollment of the certification occurs during the initial reception and integration with the Master
Trainer or upon assignment to the position if filled internally within the organization.
The Certification program starts NLT 30-days from the assignment of the position or Station
Commander Course graduation, whichever is later.
The Certification program must be completed within 180-days from the certification start date.
The Station Commander Graduation Course certificate needs to be uploaded to the USAREC G3
Training Leader Development Program SharePoint and DTMS.
Station Commanders are only required to certify once regardless of the number of stations,
regardless of a PCS to another Battalion. The Master Trainer will verify the previous record, annotate the
current record, and close the certification out.
The primary Trainer for these tasks is the First Sergeant.
The certification tasks consist of:
805K-79R-4053 Establish Intelligence Preparation of the Battlefield (IPB)
805K-79R-4054 Establish a Recruiting Functions Analysis (RFA)
805K-79R-4056 Analyze the Mission Accomplishment Plan

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 38
805K-79R-4058 Develop a Mission Accomplishment Plan (MAP)
805K-79R-4059 Implement a Station School Recruiting Program (SRP)
805K-79R-4060 Establish a Battle Rhythm
805K-79R-4061 Implement a Station Training Program
805K-79R-4063 Direct a Weekly Planning Meeting
805K-79R-4064 Direct an In-Progress Review
805K-79R-4065 Direct a Weekly After-Action Review (AAR)
805K-79R-4066 Perform Quality Control Check of an Enlistment Record
805K-79R-4067 Direct Station’s Future Soldier Training Program (FSTP)
805K-79R-4068 Perform Quality Assurance Check of Future Soldier's Record
805K-79R-4069 Assess Individual Prospecting Methods
805K-79R-4070 Establish a Station Recruiting Plan
F-3. Operations NCOIC/NCO Certification
The Operations NCOIC/NCO certification requires the Operations NCOIC and NCO to certify on 10
tasks. To qualify for the certification exam, the Ops NCOIC/NCO must:
The enrollment of the certification occurs during the initial reception and integration with the Master
Trainer or upon assignment to the position if filled internally within the organization.
The Certification program starts NLT 30-days from the assignment of the position or Guidance
Counselor Operations Course graduation, whichever is later.
The Certification program must be completed within 180-days from the certification start date.
The Guidance Counselor Operations Course certificate needs to be uploaded to the USAREC G3
Training Leader Development Program SharePoint and DTMS.
Operations NCOIC/NCO are only required to certify once. The Master Trainer will verify the previous
record, annotate the current record, and close the certification out.
The primary Trainer for these tasks is the BN Ops SGM for the OPS NCO.
The certification tasks consist of:
805K-79R-7450 Develop a Mission Accomplishment Plan (MAP)
805K-79R-7457 Process a Board Edit Request
805K-79R-7453 Perform Delayed Entry Program +10 Quality Control Procedures
805K-79R-7455 Process a Special Missions Applicant
805K-79R-7456 Process a Waiver Workflow
805K-79R-7451 Complete Opening Activities for a Recruiting Operations Office
805K-79R-7452 Complete End-of-Day Activities for a Recruiting Operations Office
805K-79R-7454 Manage the Ship without Advanced Reservation Program
805K-79R-7458 Process a Renegotiation Request
805K-79R-7459 Process a Future soldier Loss
F-4. Senior Guidance Counselor/Guidance Counselor (SGC/GC) Certification.
The Senior Guidance Counselor/Guidance Counselor certification requires the SGC and GC to
certify on 10 tasks.

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 39
The enrollment of the certification occurs during the initial reception and integration with the Master
Trainer or upon assignment to the position if filled internally within the organization.
The Certification program starts NLT 30-days from the assignment of the position or Guidance
Counselor Operations Course graduation, whichever is later.
The Certification program must be completed within 180-days from the certification start date.
The Guidance Counselor Operations Course certificate needs to be uploaded to the USAREC G3
Training Leader Development Program SharePoint and DTMS.
Senior Guidance Counselor/Guidance Counselor are only required to certify once. The Master
Trainer will verify the previous record, annotate the current record, and close the certification out.
The primary Trainer for these tasks is the BN Ops SGM for the Senior GC or Senior GC for GC.
The certification tasks consist of:
805K-79R-4302 Complete GCRc (RZ) Accession Procedures
805K-79R-4321 Complete GCRc (RZ) Enlistment Procedures
805K-79R-4323 Maintain the Applicant Background Screening (ABS) Program
805K-79R-4327 Complete Opening Procedures at an Army Liaison Office (MEPS)
805K-79R-4329 Process a Waiver
805K-79R-4330 Complete EOD Activities in an Army Liaison Office MEPS
805K-79R-4331 Prepare a Special Missions Application for Enlistment Process OCS WOFT
805K-79R-4332 Perform Quality Control Procedures
805K-79R-4334 Complete MIRS Enlistment Contract Service Certification for DEP DTP-Out
805K-79R-4335 Perform a 1.1 MIRS Projection
F-5. Senior Master Trainer/Master Trainer Certification (SMT/MT)
The Senior Master/Master Trainer certification requires the Senior Master/Master Trainer to certify
on 10 tasks. To qualify for the certification exam, the Senior Master/Master Trainer must:
The enrollment of the certification occurs during the initial reception and integration with the Master
Trainer or upon assignment to the position if filled internally within the organization.
The Certification program starts NLT 30-days from the assignment of the position or Master Trainer
Course graduation, whichever is later.
The Certification program must be completed within 180-days from the certification start date.
The Master Trainer Course certificate needs to be uploaded to the USAREC G3 Training Leader
Development Program SharePoint and DTMS.
SMT/MT are only required to certify once. The Master Trainer will verify the previous record, annotate
the current record, and close the certification out.
The primary Trainer for these tasks is the BN Ops SGM for the SMT/MT.
The certification tasks consist of:
805K-79R-4009 Conduct intelligence Preparation of the Battlefield (IPB)
805K-79R-4010 Conduct Recruiting Functions Analysis (RFA)
805K-79R-4012 Analyze the Mission Accomplish Plan (MAP)
805K-79R-4402 Assess the Team
805K-79R-4403 Manage the Organization Schools Program

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 40
805K-79R-4404 Monitor USAREC Leader Development Program and Certifications
805K-79R-4405 Plan Near-Term Training
805K-79R-4408 Manage Digital Training Management Systems (DTMS)
805K-79R-4410 Manage Unit Training Program
805K-79R-4411 Train a Recruiting Unit
F-6. Company Executive Officer Certification/Recruiting Operations Officer Certification
The Company Executive Officer (XO) / Company Recruiting Operations Officer (ROO) Certification
requires the Company XO or Company ROO to certify on nine (9) tasks.
The enrollment of the certification occurs during the initial reception and integration with the Master
Trainer or upon assignment to the position if filled internally within the organization.
The Certification program starts NLT 30-days from the assignment of the position or Company
XO/ROO Course graduation, whichever is later.
The Certification program must be completed within 180-days from the certification start date.
The Company XO/ROO certificate needs to be uploaded to the USAREC G3 Training Leader
Development Program SharePoint and DTMS.
Recruiting Company XO/ROO are only required to certify once. The Master Trainer will verify the
previous record, annotate the current record, and close the certification out.
The primary Trainer for these tasks is Company Commander or First Sergeant.
Achieve an 80% or higher on the certification exam administered at the end of each quarter.
The certification tasks consist of:
805K-79R-6001 Conduct Intelligence Preparation of the Battlefield for a Recruiting
Operational Environment
805K-79R-6002 Coordinate Company Training Plan
805K-79R-6003 Develop a Community-Centric Network
805K-79R-6004 Implement Command Supply Discipline Program
805K-79R-6005 Manage Company Operational Readiness
805K-79R-6006 Navigate Recruiting Systems
805K-79R-6007 Coordinate Company Future Soldier Training Events
805K-79R-7034/5085 Develop/Analyze Mission Accomplishment Plan
805K-79R-7035 Direct a Company School Recruiting Plan

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 41
Company XO/ROOs that pass the certification exam will earn permanent wear of the Recruiter badge.
Task numbers beginning with “CXO” do not have an associated Training & Evaluation Outline.
F-7. Company Leader Certification
The Company Leader Certification requires the Company Commander and First Sergeant to certify
in nine (9) tasks.
The enrollment of the certification occurs during the initial reception and integration with the Master
Trainer or upon assignment to the position if filled internally within the organization.
The Recruiting Company Commander/First Sergeant Course certificate needs to be uploaded to the
USAREC G3 Training Leader Development Program SharePoint and DTMS.
The Recruiting Company Commander or First Sergeant will enroll and attended the Brigade Academy
within 90 days of assumption of command/change of responsibility.
The Recruiting Company Commander or First Sergeant are only required to certify once. The Master
Trainer will verify the previous record, annotate the current record, and close the certification out.
The primary trainer for these tasks Brigade CSM or selected Senior Battalion CSM(s).
Achieve an 80% or higher on the certification exam administered at the end of each quarter.
Certification Tasks consist of:
CLC-001 Leader Development
805K-79R-7031/5008 Develop Division of Labor/Company Battle Rhythm
805K-79R-7032/5019 Conduct a Recruiting Company In-Progress Review
805K-79R-7033/5004 Conduct Market Analysis/Recruiting Functions
805K-79R-7034/5085 Develop/Analyze Mission Accomplishment Plan
805K-79R-7035 Direct a Company School Recruiting Plan
805K-79R-7037 Manage the Company Future Soldier Training Program
805K-79R-7039/5018 Develop/Implement a Company Recruiting Plan
805K-79R-5006 Monitor Unit training Program
Company Commanders that pass the certification exam will earn permanent wear of the recruiter
badge.
F-8. Battalion S-3 Officer Certification
The Battalion S-3 Officer certification requires the Battalion S-3 officer to certify on 14 tasks.
The enrollment of the certification occurs during the initial reception and integration with the Master
Trainer or upon assignment to the position if filled internally within the organization.
The Certification program starts NLT 30-days from the assignment of the position or Recruiting
Operations Officer Course (ROOC) graduation, whichever is later.
The Recruiting Operations Officer Course (ROOC) certificate needs to be uploaded to the USAREC
G3 Training Leader Development Program SharePoint and DTMS.
The primary Trainer for these tasks Brigade S-3 or Brigade Ops SGM.
The certification tasks consist of:
805K-79R-7419 Establish Operational Plan(s) in a Recruiting Environment
805K-79R-7420 Employ Waivers or Exception to Policy (ETP) Process
805K-79R-7412 Manage an Operations Staff Assisted Visit (SAV)

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 42
805K-79R-7414 Manage OCS / WOFT Program
805K-79R-7418 Coordinate Semi-Annual Reserve and Recruiting Partnership Council (R2PC)
805K-79R-7423 Manage Organizational Training
805K-79R-7410 Produce an Operational Order
805K-79R-7422 Implement the Recruiting Standards Program
805K-79R-7413 Perform a Semi-Annual Guidance Counselor Office Inspection
805K-79R-7417 Update a School Profile Evaluation
805K-79R-7415 Evaluate an Applicant’s Education
805K-79R-7409 Conduct Suitability Match Interview Procedures
805K-79R-7411 Conduct Fusion Cell Using Military Decision Making Process (MDMP)
805K-79R-7416 Manage the Unit Calendar
Battalion S-3 Officers that pass the certification exam will earn permanent wear of the recruiter badge.
F-9. Brigade S3 Officer Certification.
Brigade S3s may compete for permanent wear of the Army Recruiter Badge by completing the Recruiting
Operations Officer Course (Bde S3) and achieving a passing score of 80% or higher on the quarterly
certification exam.
F-10. Battalion Executive Officer Certification
The Battalion Executive Officer certification requires the Battalion XO to certify on six (6) tasks.
The enrollment of the certification occurs during the initial reception and integration with the Master
Trainer or upon assignment to the position if filled internally within the organization.
The Certification program starts NLT 30-days from the assignment of the position or Executive Officer
Course graduation, whichever is later.
The XO Course certificate needs to be uploaded to the USAREC G3 Training Leader Development
Program SharePoint and DTMS.
The primary trainer for these tasks Brigade XO or Brigade S-3.
The certification tasks consist of:
805K-79R-8105 Conduct the Battalion Organizational Inspection Program
805K-79R-8110 Manage a Commander’s Budget
805K-79R-8109 Manage Unit Investigations
805K-79R-8106 Direct the Battalion Staff Operation
805K-79R-8107 Manage the Battalion Recruiting Standards Program
805K-79R-8102 Manage the Battalion Staff Sections XO-01
Battalion XOs that pass the certification exam will earn permanent wear of the recruiter badge.
Task numbers beginning with “XO” do not have an associated Training & Evaluation Outline.
F-11. Brigade Executive Officer Certification.
Brigade XOs may compete for permanent wear of the Army Recruiter Badge by completing the USAREC XO
Course (Bde XO) and achieving a passing score of 80% or higher on the quarterly certification exam.
F-12. Leader Development Record Deletion
USAREC G-3 Training is the only echelon that deletes leader development records in the Leader
UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 43
Development span site. Senior master trainers will submit a Memorandum for Record (MFR) signed by the
brigade or battalion commander requesting deletion with justification.

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 44
Appendix-G
Reception and Integration
G-1. General
Establish the policy and procedures for in-processing new recruiters, officers, and company commanders.
Companies and stations are widely dispersed in the battalion’s geographical (multistate) areas, making it
difficult for many to make repeated trips to the battalion for in processing. It is imperative all soldiers are
properly sponsored and in-processed before they begin duties at their respective station or company.
G-2. Policy
The SMT/MT will initiate USAREC Form 350-1.4 (Reception and Integration Checklist) for all new
Recruiters (see Figure G-1) during the initial in-processing.
The SMT/MT will enroll all Soldiers and Officers into their applicable Leader Development Program
during the initial in-processing.
Upon completion of USAREC Form 350-1.4 for the Recruiter only, their station commanders are
required to upload it to the Recruiters ATP SharePoint record within 30 days of in-processing.
G-3. Procedures
The SMT will initiate USAREC Form 350-1.4 found in the USAREC Publications Site at Forms - All
Documents (army.mil), and complete items 1 through 15. The SMT will then e-mail the checklist to the first
scheduled staff representative who will personally brief the soldier, annotate any deficiencies, electronically
sign, and forward it to the next representative until complete.
Note: USAREC Form 350-1.4 must be printed and physically executed.
When the new Recruiter complete the initial in-processing at the battalion, the SMT will e-mail the
USAREC Form 350-1.4 to the new Recruiters Station Commander. The Station Commander will e-mail the
checklist back to the SMT within 30-days once all tasks are completed. The SMT will upload the completed
form into the Recruiters ATP record on the USAREC Leader Development Program SharePoint page as well
as into DTMS.
When new company commanders complete USAREC Form 350-1.4 (sections A through K and M) the
SMT will up-load the completed form into the Company Commander’s CLP record on the USAREC Leader
Development Program SharePoint page.
Additional spaces are available for each activity to accommodate any additional in-processing
activities in accordance with the battalion SOP.
Leaders at all levels will validate the accuracy and completion of the USAREC Form 350-1.4.

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 45
Table G-1. Sample of a completed USAREC Form 350-1.4

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 46
Appendix-H
Office of the Command Surgeon and Psychologist (OCSP) - Health, Education and
Training Program (HEAT)
H-1. General
The Health, Education and Training Program (HEAT) supports and enhances leader training and
development through the utilization of their Assessment & Selection team and the Adaptive Leader Program.
HEAT synthesizes information quelled from FM 7-22, ADP and FM 6-22, Army Resiliency Directorate, and
outside resources to support USAREC leaders in the accomplishment of their mission.
The Assessment & Selection Team contributes to the health of USAREC soldiers by participating in
field consultation on high-risk soldiers, trend analysis on predictive risk factors, and evaluation of
Recruiter/Officer candidates for suitability to USAREC and its unique stressors. These evaluations include:
Record reviews.
In-class wellness screening.
Individual interviews.
Consultations with providers.
Consolidation of completed Recruiting Candidate Assessments (RCA).
The Adaptive Leader Program integrates sport, performance and organizational psychology principles
provided through a series of instruction offered within the institutional and organizational settings. Training
objectives include but are not limited to:
Managing performance under pressure.
Identifying counter-productive communication styles and their impact on mission accomplishment.
Integration concerns.
Identification of moral and ethical challenges in the geo-dispersed environment.
Adaptive leader behaviors.
Management of high-risk soldiers.
Field Sustainment Training to meet the needs of the requestor at all levels of USAREC leadership.
These trainings may be tailored and individualized to meet the unit's needs using any sport, performance,
and organizational psychology principles.
H-2. Army Recruiter Course
Soldiers will receive the following modules aimed at promoting adaptability, self-regulation, positive leader
attributes, emotional maturity (to include tactfulness and poise) and distress tolerance for soldiers new to
USAREC.
Assessment:
Administration of in-class wellness screening and review of records and Recruiters Candidate
Assessments (RCA) to identify individuals likely to encounter difficulties meeting their medical needs in the
USAREC environment. This review prompts confidential interviews to clarify needs and ensure the individual
has a direct line of access to supports and resources in the field. A determination of suitability for USAREC is
conducted and assignments recommended in accordance with their health needs and available resources.
The Attentional and Interpersonal Style (TAIS) Inventory is a non-pathology based measure that
focuses on a recruiter's strengths and potential challenges when placed in stressful situations.
Training:
Mental Toughness: Leaders gain an understanding of how stress can affect performance in the
UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 47
recruiting environment and acquire the tools and techniques to optimize their performance within USAREC.
Tactical Awareness: Leaders explore expected challenges of becoming a Recruiter and
conceptualize these challenges within the geo-dispersed environment.
Integration: Leaders will recognize the challenges unique lo a geo-dispersed command and the
importance of successful integration of new recruiters.
Leader Engagement Tool (LET).
Academic Role-Play (ARP): As appropriate, the HEAT office will assist instructors in facilitating ARP
during end-of course labs to reinforce skills aimed at stress management.
H-3. Health Care Recruiter Course / OIC
Leader development will focus on openness to new ideas; adaptation to developing situations; handling of
unexpected demands; adapting or changing strategy; and emotion regulation. OICs, in addition to the health
care company commanders and first sergeants, will have the opportunity to engage in executive/wellness
coaching upon request. New officers and recruiters in the healthcare and chaplain professions receive the
following modules:
Assessment: Administration of wellness screening and review of records and RCA documentation.
Based on responses and need, students may be interviewed in a confidential setting to clarify needs and
support access to behavioral health resources Training: Leader Engagement Tool (LET).
Mission Essential Communication (delivered virtually / OIC only).
Executive Coaching is available upon request.
H-4. Guidance Counselor Course
The HEAT Program office does not provide training in the current program of instruction for this course.
Assessment: Wellness assessment administration and review of recruiting candidate assessment
(RCA) documentation, as necessary.
Executive Coaching is available upon request.
H-5. Assistant Station Commander Program
The HEAT office does not provide training in the current program of instruction for this program.
H-6. Station Commander Course
Soldiers receive the following modules with the focus on instilling discipline and reinforcing standards,
balancing mission with supporting wellness, understanding and implementing effective use of the Leader
Engagement Tool (LET), coping with a demanding environment, and effective self-regulation and self-care.
Assessment:
Administration of wellness screening and review of records and RCA documentation. Based on
responses and need, students may be interviewed in a confidential setting to clarify needs and support
access to behavioral health resources.
The Attentional and Interpersonal Style (TAIS) Inventory is a non-pathology based measure that
focuses on a recruiter/Officer’s strengths and potential challenges when placed in stressful situations. Station
commanders will receive individual feedback via Executive Coaching sessions and have the option to
engage in a prolonged executive coaching engagement lasting 6 months or more.
Training:
Mental Toughness.
Mission Essential Communication.
Leader Engagement Tool (LET).

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 48
Ready and Resilient (R2) overview.
Integration.
Psychological Stress and Awareness Training.
H-7. Senior Leaders Course (SLC)
Senior Leaders Course: Recruiter will attend this course prior to being promoted to Sergeant First Class.
Leader development will focus on learning Leadership Competencies, Coaching and Counseling, and other
general military subjects with the focus placed on Skill Level 4 Common Tasks. Executive Coaching is
available upon request.
H-8. Recruiting Company Commander First Sergeant Course (RCCFSC)
Company commanders and first sergeants arc central to recruiting operations and set the tone for
leadership. Leader development will focus on openness to new ideas, adaptation lo developing situations,
handling of unexpected demands, adapting or changing strategy, and emotion regulation. They will receive
the following modules:
Assessment:
Administration of wellness screening and review of records and RCA documentation. Based on
responses and need, students may be interviewed in a confidential setting to clarify needs and support
access to behavioral health resources.
The Attentional and Interpersonal Style (TAIS) Inventory is a non-pathology based measure that
focuses on a recruiting NCO/Officer’s strengths and potential challenges when placed in stressful situations.
Commanders and first sergeants will receive individual feedback via Executive Coaching sessions and have
the option to engage in a prolonged executive coaching engagement lasting 6 months or longer.
Training:
Mental Toughness.
Mission Essential Communication.
Managing Behavioral Health.
Leader Engagement Tool (LET).
H-9. Pre-Command Course (PCC)
Leaders receive education that enhances self-awareness and the challenges that recruiter/Officer, and all
levels of the operational recruiting force, face daily in the recruiting environment. They are also provided
information on the support available to them for managing high-risk soldiers in a geographically dispersed
command. They are provided the following classes:
Assessment:
Administration of wellness screening and review of records and RCA documentation. Based on
responses and need, students may be interviewed in a confidential setting to clarify needs and support
access to behavioral health resources.
The Attentional and Interpersonal Style (TAIS) Inventory is a non-pathology based measure that
focuses on a recruiter/Officer’s strengths and potential challenges when placed in stressful situations.
Leaders are given individual feedback via Executive Coaching sessions administered by the Brigade
Behavioral Health Consultant.
Training:
Managing Behavioral Health.
Adaptive Leader Program Overview.
Utilization of BDE Wellness Teams.

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 49
H-10. Recruiting Executive Office Course (ROXOC)
Leaders receive education that enhances self-awareness and the challenges that Recruiter/Officer, and all
levels of the operational recruiting force, face daily in the recruiting environment. They are also provided
information on the support available to them for managing high-risk soldiers in a geographically dispersed
command. They are provided the following classes:
Assessment:
Administration of wellness screening and review of records and RCA documentation. Based on
responses and need, students may be interviewed in a confidential setting to clarify needs and support
access to behavioral health resources.
The Attentional and Interpersonal Style (TAIS) Inventory is a non-pathology based measure that
focuses on a recruiter/Officer’s strengths and potential challenges when placed in stressful situations.
Commanders and first sergeants will receive individual feedback via Executive Coaching sessions and have
the option to engage in a prolonged executive coaching engagement lasting 6 months or longer.
Training:
Managing Behavioral Health.
Mental Toughness.
Leader Engagement Tool (LET).
Mission Essential Communication.

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 50
Appendix-I
Company/Station Training Assessment Review (CSTAR)
I-1 General
The Company/Station Training Assessment Review (CSTAR) is a mandatory quarterly template to analyze
the company or station operational capabilities and identify training needs. The CSTAR facilitates the review
of a company or stations last completed quarter data, facilitates the identification of the root cause training
deficiencies, and develops a training plan for the upcoming quarter. This flexible template allows the addition
of items for assessment and contains two parts: Part 1 for analysis and Part 2 for training plan development.
The CSTAR, (USAREC Form 350-1.6 (NPS) is located in the USAREC publication site. The use of auto
calculating CSTAR forms are authorized so long as the root cause analysis, courses of action, and training
priorities are still determined by the user manually. These types of forms can, in place of standard forms, be
uploaded into DTMS IAW this Regulation. The Medical Recruiting Brigade will use internally developed
CTARs until systems effectively support training assessments.
Administration:
The completion of the CSTAR (NPS) is mandatory for company commander/first sergeant and station
commander NLT five (5) working days following the completion of the last RSM in the quarter.
The Medical Recruiting Brigade will complete their internal CSTAR every 60-days. Brigade will
distribute data to subordinate units at the end of every 2nd calendar month for completion NLT five (5)
workings day from distribution.
The identification of operational deficiencies through the CSTAR develops the company/station
training plan and schedule. Upload training schedules in DTMS and post the CSTAR into the document
library in DTMS for higher-level approval prior to the start of the next calendar quarter (NPS and AMEDD
(IAW Appendix B).
Note: Station CSTAR uploaded into Company document library, Company CSTAR uploaded into the
Battalion document library)
The CSTAR is an inspection item.
Additional references and instructions for the CSTAR are located in USAREC TC 5-03.4, Training
and Leader Development.
Additional references and instructions for MAP Analysis are located in USAREC TC 5-03.1,
Prospecting, Processing, and Analysis.
Responsibilities:
All leadership levels:
(a) Enforce and validate the proper use of the CSTAR.
(b) Incorporate CSTAR into all inspections (virtual and physical).
Battalion Commanders/CSMs:
(a) Utilize the CSTAR to assess the validity and relevance of the company-training plan.
(b) Validate the company’s training plans matches priority training requirements within the CSTAR and
approve upon receipt but NLT 10 working days into the quarter.
(c) Review the CSTAR to identify systemic trends across the Battalion.
(d) Senior Master Trainer: Review and assess submitted CSTARs and training plans quarterly to
identify systemic training issues and provide input to the Leadership.
Company Commanders/1SG:
(a) Complete the company level CSTAR NLT 5 working days following the completion of the last RSM
of the quarter (NPS) or every 60-days for the Medical Recruiting Brigade.
(b) Use the station level CSTAR as a validation tool to validate the company’s overall assessment,

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 51
identify training gaps in specific station’s and validate that the station’s plan is relevant.
(c) Validate the stations training plans matches priority training requirements within the CSTAR and
approve.
Station commanders: Complete the station level CSTAR NLT 5 working days following the
completion of the last RSM of the quarter or W/I five (5) days of distribution from Brigade (AMEDD).
Instructions (NPS Only):
Part 1 – Operational Analysis: Part 1 (Table-I-1) is analyzing tasks against a standard, understanding
the root cause, prioritizing which deficiencies are most critical to address and developing courses of actions
to correct the problem.
Note: During task analysis, leaders use T&EOs to determine if personnel perform the tasks to a standard,
and to identify which performance measures are deficient. Instructions.
(a) Assessment Criteria: Review the assessment criteria listed and incorporate local items of interest.
(b) List the standard for each criterion from Flash to Bang and lower. These are intended for local
standards, items in gray are example standards only.
(c) List the actual results for each criterion from the last completed quarter. Only appointment made by
category will list actual MAP requirements, beyond appointment made by category all information entered
will be actual achievements from the map against the previous sections achieved. EXAMPLE: Appointment
made by category for Grad was 96 for 130 (directly from MAP), however in the CSTAR appointment made to
conduct will only count those 96 Grad appointments made against the amount of Grad conducts actual (not
required on the MAP) which is 52. In this example Grad appointment made to conduct would be 52 for 96.
(d) From the Test to Test Pass line through Floor Conversion the CSTAR will be calculated using RA
Volume, RA Grad TSC I-IIIA (GA), RA Senior TSC I-IIIA (SA), and AR Volume only.
(e) Identify the root cause for each criteria representing deficient standards.
Note: Be specific as to the root-cause as it ensures task selection meets the training need. It is important to
delineate between what is a training need and what is deficient due to non-compliance or other operational
considerations.
(f) Prioritize the criticality of the deficiency for each criteria using Red, Amber, or Green.
• Red = Critical task that must be trained immediately.
• Amber = Task that must be trained within the quarter.
• Green/Blank = No training required at this time or if time permits.
(g) The course of action is the proposed action to correct the deficiency.

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 52
Table I-1. Example USAREC Form 350-1.6 NPS CSTAR Part 1 – Operational Analysis
Part 2-Next Quarter Training Priorities: Part 2 (Table I-2) is the portion of the CSTAR that allow
leaders the ability to continue the design, begin the development, and consider implementation and
evaluation requirements within the ADDIE Process. Upon completion of Part 2, a leader should understand
how the training occurs and what to expect, (Refer to USAREC TC 5-03.4, Training and Leader
Development to review the Cognitive, Affective, and Psychomotor Domains as well as learning styles), and
the training and evaluation dates. Upon completion, transfer and upload into the Digital Training
Management System (DTMS) for submission and next higher review and approval. Instructions for CSTAR
Part 2:
(a) List the specific Training Task.
Note: If the task requires training only on a performance measure within the task, list the performance
measure and the T&EO number.
(b) List the intended outcome- What the training must accomplish. Refer to USAREC TC 5-03.4 to
review the Design phase and learning strategies, domains, and styles.
(c) List how the training takes place. Refer to USAREC TC 5-03.4 to review the Design Phase and
learning strategies, domains, and styles.
(d) List the date(s) of training. Upon the selection of dates, request facilities and transportation as soon
as tasks, outcomes, and training methodologies are known.
(e) List the date(s) the leader returns to evaluate the results of the training.
(f) Transpose results from the CSTAR to the 'Schedule Events' in DTMS. Complete and submit the

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 53
training schedule into DTMS.
Table I-2. Example USAREC Form 350-1.6 NPS CSTAR Part 2 – Next Quarter Training Priorities
NEXT QUARTER TRAINING
PRIORITIES Part 2
Training Task
Intended Outcome
Training Methodology
Date(s) of Training
Evaluation of Training
Evaluate the Market - 805K-79R-3000
Learn Market
Intelligence
Facilitation-Hands- on
6- Jul-18
10- Jul-18
Develop a Recruiter Centric
Environment-805K-79R-3007
Identify key target/locations-
CPs
Facilitation-Hands- on
13-
Jul-18
16- Jul-18
School Recruiting Program-805K-79R
-3004
Developing School SPT elements
Facilitation Hands- on
20- Jul-18
23- Jul-18
Conduct Telephone Prospecting-805K-79R-3002
Blue Printing, Pre-call,& Execution,
Hands-on Practical app
27- Jul-18
30- Jul-18
Stand Down Day
NA
NA
3- Aug-18
NA
Establish Goals and Passions- 805K-79R-3001
Develop message that resonates
Facilitation Hands- on
11- Aug-18
14- Aug-18
Influencing Techniques
Generational/cultural influence tech
Facilitation
18- Aug-18
21
- Aug-18
Engender a Commitment
Effective Closing Skills
Facilitation
25- Aug-18
28- Aug-18
School Recruiting Program-805K-79R
-3004
Developing School SPT
elements
Facilitation Hands- on
25- Aug-18
28
- Aug-18
Mandatory Training
Complete Resilience EO- AB
Facilitation
7- Sep-18
10
- Sep-18
NCOPDS /Proponent Brief
Understand all
current
Briefing
7- Sep-18
10- Sep-18
Battle Rhythm
Develop a sound Battle Rhythm
Hands-on Practical
Application
14- Sep-18
17-
Sep-18
NOTE: Each Training Task fall within the performance measures of the listed T&EO. Only the deficient portions will be
trained
NOTE: Wednesday are blocked for Station commander – Recruiting NCO Ride-Along assessment and
training

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 54
Appendix-J
Advanced Training Program (ATP)
J-1. General
The Advanced Training Program (ATP) is designed to bridge the Institutional and Organizational training
domain within USAREC. The goal of the ATP is to build upon the skills learned at the ARC and hone skills to
successfully conduct Recruiting Operations within your assigned area.
J-2. Advanced Training Program (ATP)
Policies:
The Advanced Training Program (ATP) is a pass or fail program.
The ATP is a 150-Day program starting from the day the Recruiter arrives to the Unit.
The ATP applies to all new NCOs newly assigned to Enlisted, Health Care, SORB, and Chaplain
Recruiting and NCOs returning to USAREC after a 12-month absence.
Soldiers graduating from the ARC with a first assignment to medical recruiting units, chaplain
recruiting units or special operations recruiting units will be enrolled in the ATP. The Healthcare Recruiting
Course is not required for completion of ATP.
OCONUS Soldiers ATP starts after completion of the ARC. If they PCS to their organization first, then
go to the ARC, their ATP Start Date will be the first duty day following their ARC graduation. If they go to the
ARC then PCS to their organization, their ATP State Date will be the day they sign into the organization.
Soldiers will receive training that enables them to execute recruiting tasks and TTPs for their recruiting
mission (enlisted, medical, etc.).
Station Commanders are the primary trainers of the ATP and will train, coach and mentor new
Recruiters. In the absence of a qualified Station Commander (79RV6), the First Sergeant will assume the
training responsibility for this program.
The training will be recorded on UF 350-1.2 and uploaded in the Soldier’s record in the USAREC
Leader Development Program SharePoint.
Station Commanders and First Sergeants will ensure Recruiters complete all ATP requirements and
are prepared for the BN CSM Interview to close out the ATP.
All Recruiters will conduct an interview with the BN CSM to close out their ATP. BN CSM will decide
to certify, retrain, or reassign.
NCOs enrolled in the ATP will not have unrated time in their NCO Evaluation Report.
NCOs enrolled in the ATP are not exempt from NCOPDS. ATP extension maybe authorized.
If a Soldier needs an extension for an extenuating circumstance (pregnancy, NCOPDS, major
medical injury) they may be authorized under the following provisions.
(a) Extension authorized by BN CDR.
(b) Requires a BN MFR loaded into ATP SharePoint.
(c) Authorized up to additional 90 days.
If a Soldier fails to meet the requirements to Pass ATP, additional training will be conducted.
(a) Additional training period authorized by BN CDR or BN CSM.
(b) Additional training period is a one-time authorization period.
(c) Requires a BN MFR loaded into ATP SharePoint.
(d) Authorized up to additional 90-days.
(e) Training will be initiated and continued every 30 days for 90 consecutive days.

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 55
(f) Training to be conducted by First Sergeant or Battalion Training Shop.
(g) Training will be accompanied with an associated counseling record.
The ATP is a one-time program. Commands will not use the ATP as a re-training program.
Eligibility: All recent graduates of the Army Recruiter Course will be enrolled and complete the
advanced Training Program.
Responsibilities:
USAREC G3 Training will:
(a) Coordinate with RRC to ensure all Recruiter ATP records are created at the Army Recruiter Course.
(b) Manage ATP SharePoint site.
(c) Archive completed ATP records every Fiscal Year and purge old completed records 24 months after
ATP Completion.
Battalion Commanders will:
(a) Ensure BN is complying with ATP policy and enforcing ATP standards.
(b) Complete an MFR for each Recruiter validating completion of the ATP.
(c) Manage authorization of ATP extensions.
(d) Initiate reassignment IAW AR 601-1.
Battalion CSM will:
(a) Ensure Recruiters receive adequate training and guidance.
(b) Conduct Recruiter interview within 30-days after completion of the program (Virtual, Telephonic or
In-person).
(c) Advise BN CDR on pass/fail for each Recruiter.
(d) Authorize additional training if Soldier fails ATP.
Battalion SMT/MTs will:
(a) Initiate UF 350-1.4 (Reception and Integration Form) during Recruiters in-processing with Battalion.
(b) Initiate the ATP during Recruiters in-processing. Update RSID and ATP Start Date in SharePoint
record (ATP Start Date is date soldier signed into Battalion). If no record found, create ATP record.
(c) Upload completed UF 350-1.4 into Recruiters ATP record in SharePoint. (Received from SC at the
30-day mark).
(d) Reviews all ATP Records identified as ready for BN CSM Interview for accuracy and completion.
(e) Coordinates BN CSM Interview.
(f) Manage and review ATP SharePoint records for BN actions.
(g) Closeout the ATP with results. In the situations where a record was created and a soldier did not
complete the ARC, annotate the record, and close the record.
(h) IPR with the Companies monthly on active ATP SharePoint records.
(i) Provide training assistance as needed.
Company commanders will:
(a) Ensure Company is complying with ATP policy and enforcing ATP standards.
(b) Review the ATP compliance monthly and during station inspections. Annotate within ATP record in
remarks section using the following template “-Date – Name – Comments.
Company 1SGs will:

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 56
(a) Counsel all new Recruiters within the first 30-days on expectations and consequences of the ATP.
Documented on a DA4856 and uploaded into ATP SharePoint record.
(b) Ensure Recruiters receive adequate training and guidance. Reviews and annotates within ATP
record in remarks section using the following template “-Date – Name – Comments.
(c) Close out the initial counseling that was conducted within the first 30-days at the end of the 150-Day
process.
(d) Validate Recruiter is prepared for the BN CSM Interview.
(e) Conduct ATP training in the absence of a qualified Station Commander (79RV6 – Station
Commander Course graduate).
(f) Counsel Recruiters who fail to meet ATP standards. Documented on a DA4856 and uploaded into
ATP SharePoint record.
(g) Plans, leads, and conducts additional training for the Recruiter who fails the ATP.
(h) Provide training assistance as needed.
Station Commanders will:
(a) Ensure Recruiters receive adequate training and guidance.
(b) Documents all training on UF 350-1.2. Capture what specific training was completed. Recruiters will
annotate feedback in entirety and sign the training record.
(c) Ensures Recruiters ATP SharePoint records are updated and accurate to include all admin data and
all UF350-1.2 training records.
Enrollment: All enrollments will be coordinated between G3 Training and RRC to complete initial
enrollment during the final weeks of the ARC course.
Requirements: The Station Commander will plan, prepare, and conduct training on the fundamentals
and subcategories of; Prospecting, Interview, Processing and Future Soldiers. Leaders at all levels are
expected to review and have honest conversations to what is adequate when reviewing the training that is
conducted.
Prospecting:
(a) Plan
(b) Telephonic
(c) Face-to-Face
(d) Virtual
(e) Follow-ups
(f) Referrals
Army Interview:
(a) Prepare for Army Interview
(b) Conduct Army Interview
(c) APPLEMDT
(d) Overcome Obstacle
(e) Army Story
Processing
(a) Complete electronic record
(b) Sign all required processing documents

UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 57
(c) Collect and upload all source/required documents
(d) Electronic validation
Future Soldier Management
(a) Future Soldier Orientation
(b) OPAT
(c) Follow-ups
Sustainment: Station Commanders will continuously monitor the performance and training for every
assigned Recruiter. Though ATP is a one-time program, training is an on-going responsibility of the Station
Commander.
UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 58
Glossary of Terms
Section I. Abbreviations
AAR
After-Action Review
ACS
Assistant Chief of Staff
AKO
Army Knowledge Online
ALMS
Army Learning Management System
ALTC
Annual Leaders Training Conference
AO
Area of Operations
ACFT
Army Combat Fitness Test
ARC
Army Recruiter Course
ASCP
Assistant Station Commander Program
ATC
Annual Training Conference
ATP
Advanced Training Program
ATRRS
Army Training Requirements and Resources System
BROOC
Battalion Recruiting Operations Officer Course
CLP
Company Leader Program
CG
Commanding General
CoS
Chief of Staff
CoXO
Company Executive Officer
CROOC
Company Recruiting Operations Officer Course
UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 59
CP
Community Partner
CRM
Composite Risk Management
CSM
Command Sergeant Major
CSMRC
Command Sergeant Major Recruiting Course
CSTAR
Company/Station Training Assessment Review
CTG
Command Training Guidance
DA
Department of the Army
DCG
Deputy Commanding General
DL
Distributed Learning
DTMS
Digital Training Management System
GC
Guidance Counselor
GCOC
Guidance Counselor/Operations Course
HCR
Health Care Recruiter
HCRC
Health Care Recruiting Course
HQ USAREC
Headquarters, U.S. Army Recruiting Command
HRC
U.S. Army Human Resources Command
LMS
Learning Management System
LT/LD
Leader Training and Leader Development
METL
Mission Essential Task List
UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 60
MOS
Military Occupational Specialty
MRTT
Mobile Recruiting Training Team
MT
Master Trainer
MTC
Master Trainer Course
MTT
Mobile Training Team
NCO
Noncommissioned Officer
NCODP
Noncommissioned Officer Development Program
NCOL CoE
Noncommissioned Officer Leadership Center of Excellence
NCOLDP
Noncommissioned Officer Leader Development Program
NCOPDS
Noncommissioned Officer Professional Development System
OML
Order of Merit List
OPDP
Officer Professional Development Program
PCC
Pre-Command Course
RCCFSC
Recruiting Company Commander First Sergeant Course
ROOC
Recruiting Operations Officer Course
RRC
Recruiting and Retention College
S3
Operations Officer
SCC
Station Commander Course
SCCP
Station Commander Certification Program
UR 350-1 ● 19 September 2022 61
SGC
Senior Guidance Counselor
SME
Subject Matter Expert
SMT
Senior Master Trainer
SOP
Standing Operating Procedure
SCQLD
Station commander Quarterly Leader Development
TDY
Temporary Duty
TRADOC
U.S. Army Training and Doctrine Command
TTP
Tactics, Techniques and Procedures
USAR
U.S. Army Reserve
USAREC
U.S. Army Recruiting Command
VCS
Virtual Classroom Server
VTC
Video Teleconference
XO
Executive Officer
Section II. Terms
There are no entries for this section

ELECTRONIC PUBLISHING SYSTEM
DATE: 19 SEPTEMBER 2022
DOCUMENT: USAREC REG 350-1
SECURITY: UNCLASSIFIED
DOC STATUS: EXPEDITE REVISION
USAREC

