
Understanding Process Tracing
David Collier, University of California, Berkeley
ABSTRACT
Process tracing is a fundamental tool of qualitative analysis. This method is
often invoked by scholars who carry out within-case analysis based on qualitative data, yet
frequently it is neither adequately understood nor rigorously applied. This deficit moti-
vates this article, which offers a new framework for carrying out process tracing.The refor-
mulation integrates discussions of process tracing and causal-process observations, gives
greater attention to description as a key contribution, and emphasizes the causal sequence
in which process-tracing observations can be situated. In the current period of major inno-
vation in quantitative tools for causal inference, this reformulation is part of a wider, par-
allel effort to achieve greater systematization of qualitative methods. A key point here is
that these methods can add inferential leverage that is often lacking in quantitative anal-
ysis. This article is accompanied by online teaching exercises, focused on four examples
from American politics, two from comparative politics, three from international relations,
and one from public health/epidemiology.
P
rocess tracing is a fundamental tool of qualitative
analysis. In the framework presented here,
1
it is
defined as the systematic examination of diagnostic
evidence selected and analyzed in light of research
questions and hypotheses posed by the investigator.
Process tracing can contribute decisively both to describing polit-
ical and social phenomena and to evaluating causal claims. George
and Bennett have played the leading role in developing this
method as an essential form of within-case analysis,
2
and Fenno’s
“soaking and poking” is a kindred research procedure.
3
Although the idea of process tracing is often invoked by schol-
ars as they examine qualitative data, too often this tool is neither
well understood nor rigorously applied. Relatedly, the field of qual-
itative methods in political science—in sharp contrast to quanti-
tative methods—is inadequately equipped with procedures for
teaching basic research tools, including process tracing.
This two-fold deficit motivates this article, which offers a new
framework for understanding, applying, and teaching process trac-
ing. The approach is distinctive in three ways.
ProcessTracing vis-à-vis CPOs.The evidence on which process trac-
ing focuses corresponds to what Collier, Brady, and Seawright
(2010a) call causal-process observations, or CPOs. The idea of
CPOs highlights the contrast between (a) the empirical foun-
dation of qualitative research, and (b) the data matrices ana-
lyzed by quantitative researchers, which may be called data-set
observations (DSOs). Some of the literature on which this arti-
cle draws (e.g., Brady 2010; Freedman 2010a; Mahoney 2010)
formulates arguments in terms of CPOs, rather than in terms
of process tracing per se. The present article treats these meth-
odological tools as two facets of the same research procedure.
Throughout, the article consistently refers to “process tracing”
to avoid applying two labels to what is basically the same
method.
Description. Careful description is a foundation of process tracing,
a perspective emphasized by Mahoney (2010, 125–31). Process
tracing inherently analyzes trajectories of change and causa-
tion, but the analysis fails if the phenomena observed at each
step in this trajectory are not adequately described. Hence, what
in a sense is “static” description is a crucial building block in
analyzing the processes being studied.
Sequence. Process tracing gives close attention to sequences of
independent, dependent, and intervening variables. Again, we
follow Mahoney, who has productively advanced this approach.
TEACHING EXERCISES
This new formulation of process tracing is accompanied by online
teaching exercises
4
that encompass diverse substantive areas.
a. American Politics: Fenno (1977) on members of Congress; Brady
(2010) on the 2000 Presidential election; Skocpol et al. (2000)
on civic associations; and Weaver (2007) on crime policy.
b. Comparative Politics: Lerner (1958) on social change in a Turk-
ish village; and Rogowski (2010) on the interaction of theory
and case studies.
c. International Relations: Tannenwald (1999) on the US “nuclear
taboo” after World War II; Bennett (2010) on the Fashoda cri-
sis, Germany’s expansion of military goals during World War I,
and Soviet nonintervention in Eastern Europe in 1989; and
Schultz (2001) on democracy and coercive diplomacy.
David Collier is Chancellor’s Professor of Political Science in the Department of
Political Science at the University of California, Berkeley. He can be reached at
The Teacher
.............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
doi:10.1017/S1049096511001429 PS • October 2011 823
PS: Political Science and Politics 44, No. 4 (2011): 823-30.
d. Public Health: Freedman (2010a) on major breakthroughs in
the history of epidemiology.
e. Detective Fiction: The Sherlock Holmes story “Silver Blaze”
(posted online with the exercises) serves as the basis for an
exercise, and also as a running example in parts of the follow-
ing presentation. This story is not social science, yet it provides
vivid illustrations of process tracing and is an engaging text for
teaching.
PROCESS TRACING, PRIOR KNOWLEDGE, AND DIAGNOSTIC
EVIDENCE
Process tracing, to reiterate, is an analytic tool for drawing descrip-
tive and causal inferences from diagnostic pieces of evidence—
often understood as part of a temporal sequence of events or
phenomena. Given the close engagement with cases and the cen-
trality of fine-grained case knowledge, process tracing can make
decisive contributions to diverse research objectives, including:
(a) identifying novel political and social phenomena and system-
atically describing them; (b) evaluating prior explanatory hypoth-
eses, discovering new hypotheses, and assessing these new causal
claims; (c) gaining insight into causal mechanisms; and (d) pro-
viding an alternative means—compared with conventional regres-
sion analysis and inference based on statistical models—of
addressing challenging problems such as reciprocal causation,
spuriousness, and selection bias. Thus, qualitative tools can add
leverage in quantitative analysis. They can also strengthen causal
inference in small-N designs based on the matching and contrast-
ing of cases—designs which have great value, but whose contri-
bution to causal inference urgently needs to be supplemented by
within-case analysis.
5
Process tracing requires finding diagnostic evidence that pro-
vides the basis for descriptive and causal inference. How does the
researcher establish that a given piece of evidence is diagnostic?
6
Identifying evidence that can be interpreted as diagnostic
dependscentrallyonpriorknowledge.
7
Forthepurposeoftheonline
exercises, we distinguish four interrelated types of knowledge—
extending distinctions offered by Waltz (1979), whose ideas are
important in the international relations examples included here.
Conceptual Frameworks. A first type of prior knowledge involves
sets of interrelated concepts, often accompanied by general ideas
of how the concepts can be operationalized. These frameworks
thereby identify and link the topics seen as meriting analytic
attention. The framework often points to the counterfactuals
that conceptually establish what it means for a given phenom-
enon to be absent, that is, the “contrast space” (Garfinkel 1981)
that organizes the analysis.
Recurring Empirical Regularities. These are established patterns
8
in the relationships among two or more phenomena. Waltz
(1979, 1) states that this is “not simply . . . a relationship that
has been found, but . . . one that has been found repeatedly.”
The corresponding “if a, then b” (1979, 1) connection may be
viewed as causal, or it may be understood descriptively.
Theory-I.This builds on these recurring regularities by more tightly
connecting them as a set of insights into “a particular behavior
or phenomenon” (Waltz 1979, 2). Thus, many social scientists
seek to build theory “by collecting carefully verified, intercon-
nected hypotheses.”
Theory-II. A final type of prior knowledge entails not only inter-
connected empirical regularities (Theory-I), but also a set of
statements that explain them, that is, offering explanations of
why these regularities occur (Waltz 1979, 5). Theory-II may also
be called an explanatory model.
As is clear in the exercises, some studies are explicit and pre-
cise about the prior knowledge that frames the research, whereas
for other studies it is necessary to consult a wider literature to
understand the theoretical background. Unfortunately, as inves-
tigators write up their research, they may overstate the coher-
ence of the findings vis-à-vis prior knowledge—sometimes making
it hard to identify the theoretical starting point. Reconstructing
this starting point can require detective work—which is some-
times needed in evaluating diagnostic evidence in some of the
exercises.
Against this backdrop, we consider the contribution of pro-
cess tracing to descriptive and causal inference.
DESCRIPTIVE INFERENCE
Careful description is fundamental in all research, and causal
inference—whether assessed with qualitative or quantitative tools—
depends on it.
9
Close engagement with case knowledge in pro-
cess tracing can provide a good foundation for addressing this
task.
A key point must be underscored again. As a tool of causal
inference, process tracing focuses on the unfolding of events or
situations over time. Yet grasping this unfolding is impossible if
one cannot adequately describe an event or situation at one point
in time. Hence, the descriptive component of process tracing begins
not with observing change or sequence, but rather with taking
good snapshots at a series of specific moments. To characterize a
process, we must be able to characterize key steps in the process,
which in turn permits good analysis of change and sequence.
10
Mahoney (2010, 127–28) illustrates descriptive inference in pro-
cess tracing with Tannenwald’s (1999) study of the “Nuclear
Taboo.”
11
Tannenwald argues that the horrified reaction to the
use of nuclear weapons at the end of the World War II created a
nuclear taboo that strongly influenced later US nuclear policy,
specifically decisions about the non-use of nuclear weapons dur-
ing subsequent military crises. Whereas this taboo grew out of
the reaction at the level of public opinion, it evolved into a nor-
mative mandate embraced by policy makers (1999, 462). A crucial
task in Tannenwald’s study is to establish empirically (a) that this
horrified reaction did in fact occur; (b) how widespread it was;
and (c) that the elements of this reaction did indeed add up to a
nuclear taboo. Process tracing focuses on finding and interpret-
ing diagnostic evidence that addresses these descriptive tasks. This
nuclear taboo, in turn, is the key independent variable in the study
that is evaluated vis-à-vis rival explanations of the non-use of
nuclear weapons.
Lerner’s (1958) analysis of rapid “modernization” in a Turkish
village likewise illustrates the intensive description that should
be a foundation of process tracing.
12
This transformation results
from the election of a new national governing party and the sub-
sequent introduction of infrastructure that includes electricity and
a modern road to Ankara. The transformation of the village is the
dependent variable, and the author’s goal is to describe change in
this variable over time. The analysis focuses on dozens of specific
observations of social attributes and interactions; demographic
characteristics; and material objects, physical infrastructure, and
commercial establishments.
The Teacher: Understanding Process Tracing
.............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
824 PS • October 2011

These two examples of de-
scription differ in important
ways. Tannenwald relies on di-
verse primary and secondary
sources—including official doc-
uments, memoirs, and biogra-
phies—that shed light on the
politics of nuclear policy mak-
ing. By contrast, Lerner’s study
depends on intensive interview-
ing, carried out by his field assis-
tants. Further, as noted, the
phenomenon described through
process tracing is Tannenwald’s
main independent variable; thus,
the nuclear taboo is her hypoth-
esized explanation for the US
post-World War II non-use of
nuclear weapons. By contrast,
for Lerner the posited modern-
ization of the village is the
dependent variable triggered by
an electoral shift and the initia-
tive of the victorious party to
build new infrastructure. Finally, while both Lerner and Tannen-
wald offer a rich and detailed description of a key variable, Tan-
nenwald also gives substantial attention to rival explanations.
The two examples also illustrate another point: The qualita-
tive researcher should recognize that the fine-grained descrip-
tion in process tracing sometimes relies on quantitative data.
This is certainly reasonable, given that—in the spirit of pursu-
ing multi-method research—the boundary between qualitative
and quantitative should not be rigid.
13
For Lerner, some of the
information is demographic, involving numerical data. As seen
in the exercises, Brady’s (2010) process tracing study employs
quantitative data on elections and voting. In parallel, Tannen-
wald could have assessed the pervasiveness of horrified reactions
by counting their overall frequency, different types of horrified
reactions, and change in these counts over time. Process tracing
does indeed focus on single “nuggets” of information, yet some-
times this information involves counts and not just single actions
or occurrences.
A different form of description, based on counterfactuals, is
illustrated by the Sherlock Holmes story “Silver Blaze.” Here the
central puzzle
14
is to explain the murder of John Straker, trainer
of the racehorse Silver Blaze. The focus is on a singular event that
cannot be disaggregated—a focus also common in process-tracing
research in international relations. With singular events, descrip-
tion may be based on comparison of the observed value of a given
variable with one or more hypothetical—i.e., counterfactual
15
—
values that are seen as plausible alternatives, but that do not occur
in the case being studied. The comparison depends on the con-
trast space noted above, which builds on the researcher’s back-
ground knowledge. Counterfactuals are important in diverse areas
of research (e.g., King, Keohane, and Verba 1994, 77–78, 88–89),
and they play a particularly visible role here.
CAUSAL INFERENCE
Basic ideas about applying process tracing to causal inference
may be summarized in terms of four empirical tests. Slightly
adapting the formulation of Bennett (2010), who builds on the
work of Van Evera (1997), the tests are classified according to
whether passing the test is necessary and/or sufficient for accept-
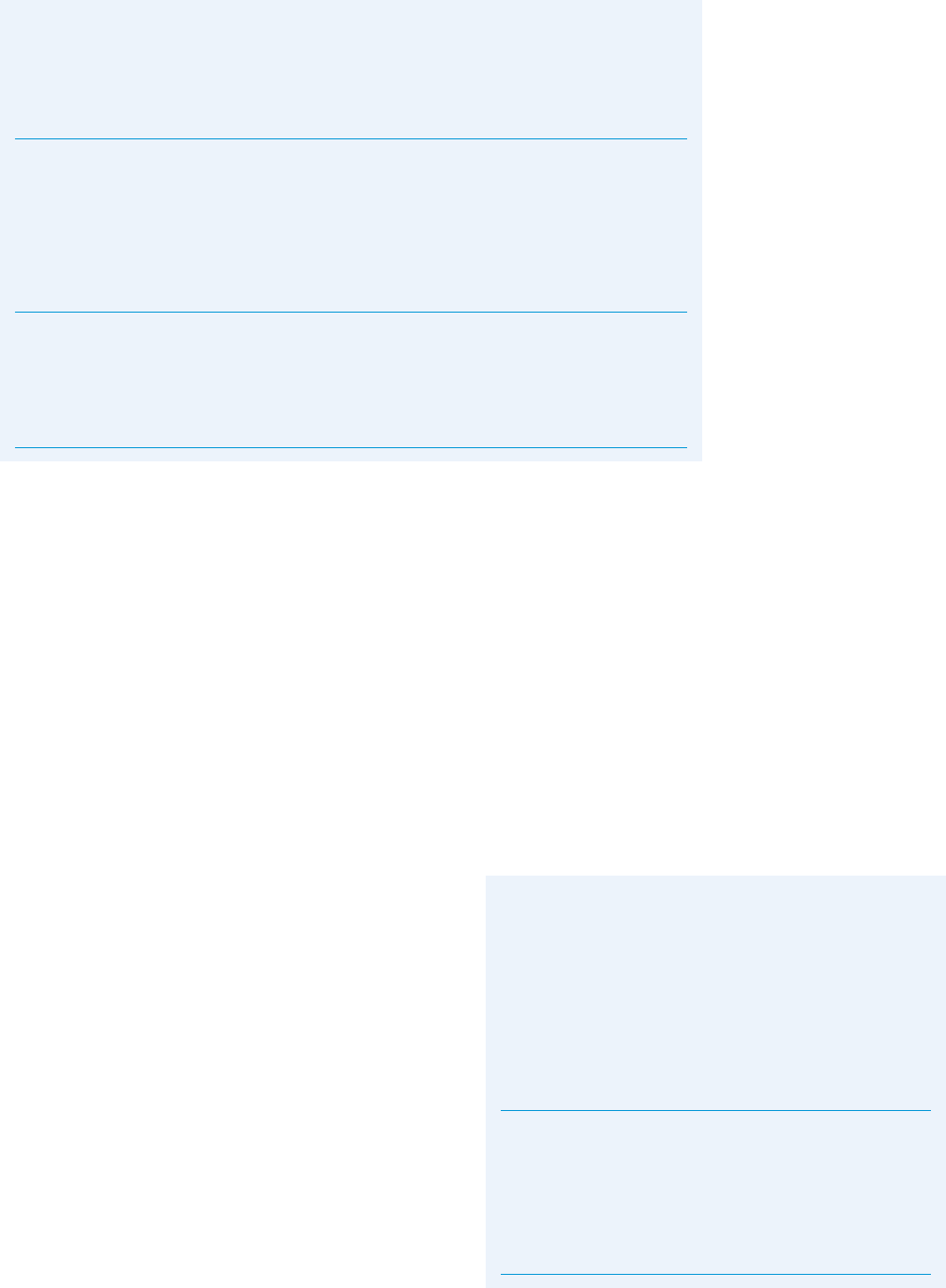
ing the inference. Based on these criteria, table 1 presents the
four tests: straw-in-the-wind, hoop, smoking-gun, and doubly deci-
sive. The table also notes the implications for rival hypotheses of
passing each test. If a given hypothesis passes a straw-in-the-
wind test, it only slightly weakens rival hypotheses; with hoop
tests it somewhat weakens them; with smoking-gun tests it sub-
stantially weakens them; and with doubly decisive tests passing
eliminates them—of course, with the usual caveat that the defin-
itive elimination of a hypothesis is often hard to achieve in social
science.
Before we introduce causal inference, it is useful to reiterate
two ideas discussed above: process tracing can focus either on
recurring events or on a singular event; and although it is reason-
able to think of process tracing as a qualitative method, it some-
times relies on quantitative information.Three other points should
also be emphasized:
Specification of Hypotheses. Careful, analytically informed specifi-
cation of hypotheses is essential both in selecting and inter-
preting pieces of evidence, and in weighing them against one
another. Background knowledge is fundamental here.
Distinctions among Tests. The distinctions in table 1 are a use-
ful heuristic, but should not be taken rigidly. The decision to
treat a given piece of evidence as the basis for one of the
four tests can depend on the researcher’s prior knowledge,
the assumptions that underlie the study, and the specific
formulation of the hypothesis. Although in general the ap-
propriate test is clear, sometimes a piece of evidence treated
as a straw-in-the-wind might instead be viewed as the basis
for a hoop test or a smoking-gun test (see tables 4 and 5
below). Alternatively, it might simply be viewed as an “inter-
mediate” test, with corresponding implications for rival
hypotheses.
Table 1
Process Tracing Tests for Causal Inference
SUFFICIENT FOR AFFIRMING CAUSAL INFERENCE
No Yes
NECESSARY
FOR
AFFIRMING
CAUSAL
INFERENCE
Source:
Adapted from Bennett ~2010, 210!, who builds on categories formulated by Van Evera ~1997, 31–32!.
No
Yes
1. Straw-in-the-Wind 3. Smoking-Gun
a. Passing: Affirms relevance of hypothesis,
but does not confirm it.
a. Passing: Confirms hypothesis.
b. Failing: Hypothesis is not eliminated, but
is slightly weakened.
b. Failing: Hypothesis is not eliminated,
but is somewhat weakened.
c. Implications for rival hypotheses:
Passing
slightly
weakens them.
Failing
slightly
strengthens them.
c. Implications for rival hypotheses:
Passing
substantially
weakens them.
Failing
somewhat
strengthens them.
2. Hoop 4. Doubly Decisive
a. Passing: Affirms relevance of hypothesis,
but does not confirm it.
a. Passing: Confirms hypothesis and
eliminates others.
b. Failing: Eliminates hypothesis. b. Failing: Eliminates hypothesis.
c. Implications for rival hypotheses:
Passing
somewhat
weakens them.
Failing
somewhat
strengthens them.
c. Implications for rival hypotheses:
Passing
eliminates
them.
Failing
substantially
strengthens.
.............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
PS • October 2011 825
Assumptions and Interpretations. The decision about which test
is appropriate to a particular piece of evidence thus in-
volves different assumptions and interpretations.
16
For
example, if researchers make the weaker assumption that a
given event (or other piece of evidence) may be a coincidence,
they should and will be more cautious. Alternatively, if
they make the stronger assumption—based on prior
knowledge—that it is probably not a coincidence, they may
arrive at a different conclusion about accepting or rejecting
the hypothesis.
17
Against this backdrop, we discuss the four process-tracing tests
in table 1, using the Sherlock Holmes story “Silver Blaze” as a
running example. At this point it may be useful for readers to
examine the story itself.
Mapping the Holmes story onto the framework presented ear-
lier, we might say that the suspects are in effect the hypotheses,
and the clues are causal process observations (CPOs). Table 2 pro-
vides an overview of the story and presents the hypotheses used
in illustrating the four tests, organized according to whether they
concern an independent, intervening, or dependent variable. As
indicated in the table, the mystery contains two causal puzzles:
explaining the murder of John Straker and the disappearance of
the horse. The following examples concentrate on the murder,
and references to the horse’s disappearance are considered when
crucial to the murder itself.
Straw-in-the-Wind Tests
These tests, illustrated in table 3, can increase the plausibility of
a given hypothesis or raise doubts about it, but are not decisive
by themselves. Straw-in-the-wind tests thus provide neither a
necessary nor a sufficient criterion for accepting or rejecting a
hypothesis, and they only slightly weaken rival hypotheses. Of
the four tests, these are the weakest and place the least demand
on the researcher’s knowledge and assumptions. Yet they pro-
vide valuable benchmarks in an investigation by giving an initial
assessment of a hypothesis. Furthermore, if a given hypothesis
passes multiple straw-in-the-
wind tests, it adds up to impor-
tant affirmative evidence.
In “Silver Blaze,” one straw-
in-the-wind is based on the
clues about the bill for expen-
sive women’s clothing found in
Straker’s pocket and Straker’s
wife’s ignorance of the costly
dress that had been purchased.
This lends weight to Holmes’s
suspicion about Straker’s role
(H1) and to the idea that Straker
might have had a financial
motive for throwing the race,
but is not by itself a decisive
piece of evidence. Another
straw-in-the-wind is one of the
most famous clues in all of
detective fiction: that the dog
presumably guarding the
horse’s stable “did nothing in
the night,” an observation that
points to the possibility that someone known to the dog—i.e.,
Straker—abducted the horse (H3). Yet it certainly does not con-
firm this hypothesis.
Hoop Tests
Hoop tests (table 4) set a more demanding standard. The hypoth-
esis must “jump through the hoop” to remain under consider-
ation, but passing the test does not by itself affirm the hypothesis.
Although not yielding a sufficient criterion for accepting the expla-
nation, it establishes a necessary criterion. Hoop tests do not
confirm a hypothesis, but they can eliminate it. Compared to the
straw-in-the-wind tests, passing hoop tests has stronger implica-
tions for rival hypotheses: it somewhat weakens their plausibility,
without precluding the possibility that alternative hypotheses may
be relevant.
Table 2
Overview of “Silver Blaze”
Causal Puzzle
To explain the murder of John Straker and, secondarily, the disappearance and whereabouts of the racehorse
Silver Blaze.
Main Characters
Silver Blaze
, the racehorse that is the favorite for the Essex Cup, has disappeared.
John Straker
, the horse’s trainer, has been killed by a terrible blow that shattered his head.
Fitzroy Simpson
, a prime suspect, has been lurking around the stable seeking inside information about the
race.
Ned Hunter
, a stable boy, has been drugged with opium concealed in curried mutton. He therefore fails to guard
Silver Blaze on the night of the horse’s disappearance.
Colonel Ross
is the owner of King’s Pyland Stables and of Silver Blaze.
Hypotheses
Independent Variables Intervening Variables Dependent Variables
H1. Romantic entanglement
started chain of events
H3. Straker abducted horse H6. Simpson killed Straker
H2. Chain of events started in
Straker household
H4. Straker planned to harm
horse
H7. Straker killed himself
H5. Straker practiced the injury
H8. Horse killed Straker
Table 3
Straw-in-the-Wind Tests
H1. Straker’s romantic entanglement set chain of events into motion.
Clues. A bill from an expensive women’s clothing store is found in Strak-
er’s pocket, and his wife is ignorant of the clothing in question.
Inference. The bill was owed by Straker for an expensive gift to another
woman, and Straker may have been in financial difficulty. This could
give him a motive for throwing the race.
Summary. This promising lead, a
straw-in-the-wind
, lends weight to H1,
but is not by itself a decisive piece of evidence.
H3. Straker abducted the horse.
Clue. The dog did nothing ~i.e., did not bark! in the night during which the
horse disappeared.
Inference. The person who approached the stable, possibly Straker, was
well-known to the dog. This raises questions about why Straker might
have gone to the stable. It suggests that perhaps he came to abduct
the horse, but does not strongly demonstrate this.
Summary. This
straw-in-the-wind
favors H3, but does not confirm it.
The Teacher: Understanding Process Tracing
.............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
826 PS • October 2011

Table 4 presents two hoop tests, both focused on the hypoth-
esis that Simpson killed Straker (H6). Simpson carried a poten-
tial murder weapon, so that he passes the corresponding hoop
test and is therefore not precluded as a suspect. However, his timid,
non-menacing appearance might seem to preclude his being a
murderer who “shattered” Straker’s head with a “savage” blow.
Hence, he fails this second hoop test. Table 4 also illustrates alter-
native interpretations of the same piece of evidence. One could
assume, as just stated, that a timid individual such as Simpson
would never commit a savage murder—thereby eliminating him
as a suspect through the hoop test. Alternatively, it may be unlikely,
but definitely not impossible, that a timid and nonmenacing per-
son would commit such a murder. This would yield a straw-in-
the-wind that casts doubt on the idea that that he is the murderer—
yet he remains a possible suspect.
Smoking-Gun Tests
The metaphor of a “smoking gun” conveys the idea that a suspect
who is caught holding a smoking gun is presumed guilty. How-
ever, those with no smoking gun may not be innocent. In other
words, this provides a sufficient but not necessary criterion for
accepting the causal inference. It can strongly support a given
hypothesis, but failure to pass does not reject it. If a given hypoth-
esis passes, it substantially weakens rival hypotheses.
In “Silver Blaze,” the first smoking-gun test (table 5) is straight-
forward. The fact that the maid brought the curried mutton to
the stable shows that the initiative to drug the stable boy—a key
step in the chain of events—had to begin in Straker’s household
(H2). By contrast, the hypothesis that Straker planned to cause
harm (H4) is ambiguous and illustrates the importance of prior
knowledge and assumptions. Depending on such knowledge and
assumptions, the knife found with Straker can be viewed as
extraordinarily odd and suspicious, or only somewhat unusual.
Accordingly, the knife is alternatively a smoking-gun or a
straw-in-the-wind.
Doubly Decisive Tests
These tests provide strong inferential leverage that confirms one
hypothesis and eliminates all others. They meet both the neces-
sary and sufficient standard for establishing causation. As Ben-
nett (2010, 211) notes, single tests that accomplish this are rare in
social science, but this leverage may be achieved by combining
multiple tests, which together support one explanation and elim-
inate all others.
Turning again to the Sherlock Holmes example (table 6), we
see that Simpson, Straker, and the horse are suspects in Straker’s
death. Simpson (H6) and Straker (H7) are removed from suspi-
cion by hoop tests. Based on straw-in-the-wind tests, one of which
might be interpreted as a smoking-gun test, Holmes infers that
the horse kicked Straker, thereby inflicting the grievous blow that
shattered his head. The conjunction of these diverse tests serves
to eliminate other suspects and establish the horse’s guilt (H8),
thereby meeting the standard of both necessity and sufficiency.
Combining tests in this way poses important challenges. Cen-
tral here is Holmes’s method of elimination, a strategy invoked var-
ious times in Doyle’s stories. Put simply, when the investigator
has eliminated all plausible alternatives, the remaining scenario
must be the correct one. Variants of this method are widely recog-
nized, as with eliminative induction in Bayesian analysis (Vineberg
1996) and J.S. Mill’s (1974, 397–98) method of residues.
The method of elimination is especially relevant here because
although two suspects are definitely eliminated through hoop tests,
the guilt of the horse is established primarily on the basis of weaker
straw-in-the-wind tests. The procedure of elimination is valuable
because it relies centrally on the definitive exoneration of the first
two suspects, and only secondarily on explicit demonstration of
the horse’s guilt.
Further, the method of elimination has special relevance to
the case of Silver Blaze, given that both Mill (1974, 398) and
Holmes emphasize the value of this method for discovering
unusual or even bizarre explanations—such as the kick of the horse
as a murder weapon (see table 6, H8, inference d). Mill states that
among his methods, “this is the most fertile in unexpected results”
(p. 398), and as Holmes puts it, “when you have eliminated the
impossible, whatever remains, however improbable, must be the
Table 4
Hoop Tests
H6. Simpson killed Straker.
Clue. Simpson had a potential murder weapon.
Inference. This weapon is consistent with the hypothesis, but does not
by itself demonstrate Simpson’s guilt.
Summary. Simpson had a potential weapon, so H6 passes this
hoop
test.
H6. Simpson killed Straker.
Clues. Simpson’s timid, non-menacing appearance, plus the fact that
Straker’s “head had been shattered by a savage blow from some heavy
weapon.”
Inference. With a stronger assumption based on his appearance, Simp-
son could not have inflicted the blow that shattered Straker’s head.
Alternative Inference. With a weaker assumption, Simpson’s appear-
ance raises doubts that he would have committed the murder, but does
not preclude it.
Summary. With a stronger assumption this is a
hoop
test which H6 fails;
with a weaker assumption it is a
straw-in-the-wind
test which casts
doubt on H6.
Table 5
Smoking-Gun Tests
H2. The chain of events started in Straker’s household.
Clues. The household maid brought the stable boy curried mutton, and
he was found later to have been drugged.
Inference. The curry was served to conceal the opium, which in turn was
used to drug the stable boy. When it is clear that the curry could only
have been introduced in the mutton by someone in Straker’s house-
hold, members of his household become inextricably linked to a key
causal step.
Summary. The clues yield a
smoking-gun
test that confirms H2.
H4. Straker planned to harm the horse.
Clue. Unusual, surgical knife found with Straker.
Inference: The knife is interpreted as
exceptionally
unusual—establishing
intent to harm.
Alternative Inference: The knife is interpreted as
somewhat
unusual,
suggesting, but hardly confirming, intent to harm. It might possibly be
a coincidence.
Summary. If the knife is exceptionally unusual, it is a
smoking gun
that
confirms H4. With a weaker interpretation that the knife was somewhat
unusual, it is a
straw-in-the-wind
that makes H4 more plausible, with
out confirming it.
.............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
PS • October 2011 827

truth. . . .”
18
In contemporary political science, a recurring con-
cern is that the discipline needs tools for discovering unexpected
and unusual explanations.The method of elimination merits atten-
tion as precisely this kind of tool.
19
Causal-Sequence Framework: Auxiliary Outcome Test
Another test is suggested by Mahoney’s (2010, 125–31) causal-
sequence framework. He introduces the idea of auxiliary out-
comes, which are not part of the main causal sequence yet provide
valuable inferential leverage.
20
Fruitful theories generate multi-
ple observable implications (King, Keohane, and Verba 1994,
passim), and a particular independent variable or mechanism
hypothesized to influence the dependent variable may also
affect an auxiliary outcome. The inference thereby derived
may further support the causal importance of the independent
variable or intervening mechanism. In “Silver Blaze,” the lame
sheep are an example of an auxiliary outcome (table 7). Holmes
infers that Straker wished to practice the delicate operation
required to injure the horse (H5). This does not directly injure
the horse; it is a secondary outcome that makes Holmes’s ideas
about the central causal process more plausible. Auxiliary out-
come tests generally yield straws-in-the-wind, as occurs in this
example.
Mahoney further illustrates the auxiliary outcome test with a
social science example: Luebbert’s (1991) famous book, Liberal-
ism, Fascism, or Social Democracy. Luebbert’s central argument is
that a “red-green” coalition of socialist parties and the middle
peasantry was a key factor in the formation of national-political
economies in interwar Europe. Mahoney shows that while this
claim is partly developed through small-N comparative research
and partly through a focus on mechanisms, Luebbert also builds
his case by arguing that if a red-green alliance really did foster
social democracy, it should have left behind other markers, includ-
ing the reluctance of socialists to challenge the distribution of
wealth in the countryside (Mahoney 2010, 130). The discovery of
such auxiliary outcomes suggests that the red-green alliance had
a key impact on other domains of national politics. This finding
reinforces the idea that the alliance was highly influential, yield-
ing stronger grounds for inferring that it also shaped the national
political-economic regime (Mahoney 2010, 130).
CONCLUSION
This article seeks to improve the practice of process tracing as a
strategy of qualitative analysis, a strategy that can also contribute
to quantitative research. The discussion is accompanied by the
online exercises focused on ten empirical studies, from diverse
subfields, aimed at encouraging careful thinking—and productive
teaching—about process tracing.
Three concluding points merit emphasis. First, as Brady, Col-
lier, and Seawright (2010, 22) note, “both qualitative and quanti-
tative research are hard to do well.” Qualitative tools such as
process tracing can address some challenges faced in quantitative
analysis, but process tracing faces serious issues in its own right.
21
Doubts may arise as to which causal-inference test is appropriate.
The analysis may face standard problems of missing variables.
Measurement error can be an issue, and probabilistic relation-
ships are harder to address than in quantitative research. This
article is intended as one step in developing and refining tools for
process tracing—and it is urgent that it not be the last step. More
work must be done.
Second, in a given study, how does one begin to carry out pro-
cess tracing? It is certainly valuable to approach process tracing
with the expectation of using the causal inference tests presented
in table 1, yet these tests are not always easy to apply. It can there-
fore be productive to start with a good narrative or with a timeline
that lists the sequence of events. One can then explore the causal
ideas embedded in the narratives, consider the kinds of evidence
Table 6
Building a Doubly Decisive Test by
Evaluating Alternative Hypotheses
H6. Simpson killed Straker.
Clues. The household maid brought the stable boy curried mutton, and
he was found later to have been drugged.
Inference. The curry served to conceal the opium, which in turn was
used to drug the stable boy. Because the curry could only have been
introduced in the mutton by someone in Straker’s household, Simpson
is excluded from consideration.
Summary for H6. This
hoop
test rejects H6, eliminating Simpson as a
suspect.
H7. Straker killed himself.
Clue. Straker’s head was “shattered by a savage blow from some heavy
weapon.”
Inference. Straker could not have shattered his own head with such a
blow.
Summary for H7. This
hoop
test rejects H7, eliminating Straker as a
suspect.
H8. The horse killed Straker.
Clues. ~a! Bill in Straker’s pocket and wife’s ignorance of dress; ~b! Strak-
er’s unusual surgical knife; ~c! matches and candle, and the horse dis-
appeared at night; ~d! the unusual form of death—Straker’s head was
“shattered by a savage blow from some heavy weapon.”
Inferences. ~a! Straker’s romantic entanglement and resulting financial
difficulty provided a motive to throw the race ~
straw-in-the-wind
, table
3!; ~b! Straker planned to harm the horse ~
smoking gun
or
straw-in-the-
wind
, table 5!; ~c! when Straker attempted to harm the horse at night,
the candle and prick of the knife frightened the horse and led to a fatal
kick ~
straw-in-the-wind
!; ~d! the unusual form of death ~savage blow!
points to an extreme or unusual cause, i.e., the horse’s kick ~
straw-in-
the-wind
!.
Summary for H8. The combined weight of four
straws-in-the-wind
, one
of which may be a
smoking gun
, strongly favor the hypothesis that the
horse killed Straker.
Summary of Doubly Decisive Test. Two of the three suspects are elim-
inated by
hoop
tests, leaving only the horse. A series of additional infer-
ences strongly implicate the horse. The combined weight of evidence
confirms H8, that the horse killed Straker.
Table 7
Auxiliary Outcome
H5. Straker practiced in preparation for injuring the horse.
Clue. Lame sheep.
Inference. Straker used the sheep to practice a delicate operation with
his surgical knife—which he planned to use for inflicting an undetect-
able injury to the horse. The inference is not that the sheep’s lameness
is a step in the central explanatory chain; rather lends further support
to Holmes’s understanding of that chain
Summary. The lameness is a
straw-in-the-wind
that favors H5 without
confirming it.
The Teacher: Understanding Process Tracing
.............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
828 PS • October 2011

that may confirm or disconfirm these ideas, and identify the tests
appropriate for evaluating this evidence.
Finally, along with the value per se of refining process tracing,
this discussion is important in wider debates on political meth-
odology. Political science is in a period of major innovation in
refining tools for quantitative analysis, and in particular, quanti-
tative tools for causal inference. This trend has produced some
worries among qualitative researchers about the adequacy of their
own tools, and perhaps it has intensified the skepticism of some
quantitative researchers about causal inference in qualitative stud-
ies. This skepticism led the eminent statistician David Freedman
(2010a) to counter with the argument that the kind of qualitative
analysis involved in process tracing is indeed a type of scientific
inquiry in its own right. In that spirit, the goal here is to take
steps toward placing this form of inquiry on a more rigorous
foundation.
䡲
NOTES
Among the several colleagues who provided valuable comments on this article, Maria
Gould and three anonymous reviewers for PS deserve special thanks.
1. The approach discussed here differs from other research traditions that can be
linked to the idea of process tracing—for example, the work on mechanisms of
Tilly (2001) and McAdam, Tarrow, and Tilly (2001).
2. Within-case analysis can become multi-case analysis if different facets of the
initial “case” are analyzed. The key idea here is that the point of departure is a
single case, when viewed from the perspective of a wider comparative analysis
focused on a larger N.
3. George (1979); George and McKeown (1985); George and Bennett (2005);
Bennett (2008, 2010). On “soaking and poking,” see Fenno (1977, 884; 1978,
xiv; 1998, v). Process tracing has much in common with Lazarsfeld’s (1940,
preface) procedure of “discerning”; Campbell’s (1975, 181–82) “pattern match-
ing,” which is also advocated by Yin (1984/2008); Sewell’s (1996, 261) “causal
narrative”; Bates et al.’s (1998) “analytic narratives”; and Hall’s (2003, 391–95)
“systematic process analysis.”
4. See ^tinyurl.com/DavidCollier&.
5. Ideas about these designs based on a matching of cases are often drawn from
J.S. Mill (1974) and Przeworski and Teune (1970). For a comment on the
weakness of these designs for causal inference, see Collier, Brady, and Sea-
wright (2010a, 10).
6. Addressing this question raises issues about the logic of inquiry and the form
of social scientific knowledge that are well beyond the scope of this discus-
sion. Only a few basic points are addressed here that are salient for the accom-
panying exercises.
7. Obviously, such prior knowledge is essential in all research, both qualitative
and quantitative.
8. Waltz calls claims about these regularities “law-like statements” (p. 1). We
prefer the alternative label used here.
9. The expressions “descriptive inference” and “causal inference” are employed
here in the sense of King, Keohane, and Verba (1994, 7–8, chaps. 2–3). Their
usage can be seen as approximating an ordinary language meaning of “de-
scription” and “causation”; and by “inference” they mean that researchers
have “the goal of making inferences that go beyond the particular observa-
tions collected,” that is, they are analyzed within the larger framework used
by the investigator. This usage contrasts with ideas of “descriptive inference”
and “statistical inference” that are standard in the work of statisticians (e.g.,
Berk 2004, chap. 11).
10. Achieving good description in this sense, and developing fruitful ideas about
the unfolding of the process, may of course interact in an iterative manner.
11. Tannenwald’s study is also discussed in Collier, Brady, and Seawright (2010a,
189–90; 2010b, 509).
12. Lerner’s analysis—which is the focus of one of the exercises—is closely tied to
modernization theory, which might concern some readers; and at certain
points the presentation seems condescending. Further, the female interviewer
is presented in a sexist way (although in survey research, selecting interview-
ers in light of characteristics such as these is widely recognized as important).
However, these drawbacks are outweighed by the opportunity presented by
the chapter to illustrate the practice of making careful observations, and also
to see how they can be integrated into a complex picture of social change.
13. For a framing of qualitative vis-à-vis quantitative in terms of four dimensions,
see Collier, Brady, and Seawright (2010a, 177–82).
14. Another puzzle is explaining the disappearance of the horse, but as Holmes
himself emphasizes, that is a secondary issue (see p. 11 in the accompanying
online version of the story).
15. See Levy’s (2008) excellent discussion of counterfactuals and case studies.
16. There is a parallel here to the idea in statistical work that the test does not
stand on its own, but rather is shaped by prior assumptions. In quantitative
analysis, the construction of the statistical model depends heavily on such
assumptions, and in general the statistical test does not directly evaluate these
assumptions. Rather, it estimates the relationship based on the supposition
that the model assumptions, as well as the underlying assumption of causal-
ity, are true. See, for example, Freedman (2010b).
17. In one story, Sherlock Holmes takes a strong stand on coincidences (“Adven-
ture of the Second Stain”; in Doyle 1960, this is on p. 655). Watson refers to
the juxtaposition of two key events as “an amazing coincidence.” Holmes
replies: “A coincidence! The odds are enormous against its being a coinci-
dence. No figures can express them. No, my dear Watson, the two events are
connected—must be connected. It is for us to find the connection.” Ironically,
it turns out that these two events are only tangentially connected, so Watson’s
statement was closer to the truth than Holmes’s, and the weaker assumption
was more appropriate. In another story, Holmes is initially more cautious
about inferences and coincidences, but then he backtracks and insists on the
certitude of his inferences (“The Sign of Four,” chap. 1; in Doyle 1960, this is
on p. 93).
18. “The Sign of Four,” chap. 6 (in Doyle 1960, this is on p. 111).
19. A further perspective on unusual or bizarre explanations (see again table 6,
H8, inference d) derives from William James’s famous dictum that “every
difference must make a difference.” To put this in a less extreme form, it
might be said that some differences make a difference. In this instance, the
form of the murder was so distinctive that it called for a distinctive
explanation—which turned out to be the kick of a horse. On William James,
see Copi (1953, 331–32).
20. Andrew Bennett (personal communication) has underscored the parallel here
with diagnostic tests in medicine.
21. Waldner (2011) offers an interesting discussion of such issues.
REFERENCES
Bates, Robert H., Avner Greif, Margaret Levi, Jean-Laurent Rosenthal, and Barry
Weingast. 1998. Analytic Narratives. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Bennett, Andrew. 2008. “Process Tracing: A Bayesian Perspective.” In The Oxford
Handbook of Political Methodology, ed. Janet M. Box-Steffensmeier, Henry E.
Brady, and David Collier, 702–21. New York: Oxford University Press.
Bennett, Andrew. 2010. “Process Tracing and Causal Inference.” In Rethinking
Social Inquiry: Diverse Tools, Shared Standards, 2nd ed., ed. Henry E. Brady and
David Collier, 207–19. Lanham, MD. Rowman and Littlefield.
Berk, Richard A. 2004. Regression Analysis: A Constructive Critique. Newbury Park,
CA: Sage.
Brady, Henry E. 2010. “Data-Set Observations versus Causal-Process Observations:
The 2000 U.S. Presidential Election.” In Rethinking Social Inquiry: Diverse Tools,
Shared Standards, 2nd ed., ed. Henry E. Brady and David Collier, 237–42. Lan-
ham, MD: Rowman and Littlefield.
Brady, Henry E., David Collier, and Jason Seawright. 2010. “Refocusing the Discus-
sion of Methodology.” In Rethinking Social Inquiry: Diverse Tools, Shared Stan-
dards, 2nd ed., ed. Henry E. Brady and David Collier, 15–31. Lanham, MD:
Rowman and Littlefield.
Campbell, Donald T. 1975. “‘Degrees of Freedom’ and the Case Study.” Compara-
tive Political Studies 8 (2) : 178–93.
Collier, David, Henry E. Brady, and Jason Seawright. 2010a. “Sources of Leverage
in Causal Inference: Toward an Alternative View of Methodology.” In Rethink-
ing Social Inquiry: Diverse Tools, Shared Standards, 2nd ed., ed. Henry E. Brady
and David Collier, 161–99. Lanham, MD: Rowman and Littlefield.
Collier, David, Henry E. Brady, and Jason Seawright. 2010b. “Outdated Views of
Qualitative Methods: Time to Move On.” Political Analysis 18 (4) : 506–13.
Copi, Irving M. 1953. Introduction to Logic. New York: Macmillan.
Doyle, Arthur Conan. 1960/1986. The Complete Sherlock Holmes, Vol. 1 and 2. New
York: Doubleday. The 1986 edition (New York: Bantam Classics) is available in
paperback, and all the stories are readily available online.
Fenno, Richard F., Jr. 1977. “U.S. House Members in Their Constituencies: An
Exploration.” American Political Science Review 71 (3): 883–917.
Fenno, Richard F., Jr. 1978. Home Style: House Members in their Districts. Boston:
Little, Brown.
Fenno, Richard F., Jr. 1998. Senators on the Campaign Trail: The Politics of Represen-
tation. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press.
.............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
PS • October 2011 829
Freedman, David A. 2010a. “On Types of Scientific Inquiry: The Role of Qualita-
tive Reasoning.” In Rethinking Social Inquiry: Diverse Tools, Shared Standards,
2nd ed., ed. Henry E. Brady and David Collier, 221–36. Lanham, MD: Rowman
and Littlefield.
Freedman, David A. 2010b. Statistical Models and Causal Inference: A Dialogue with
the Social Sciences. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Garfinkel, Harold. 1981. Forms of Explanation. Rethinking the Questions in Social
Theory. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press.
George, Alexander L. 1979. “Case Studies and Theory Development: The Method
of Structured, Focused Comparison.” In Diplomacy: New Approaches in History,
Theory and Policy, ed. Paul Gordon Lauren, 43–68. New York: The Free Press.
George, Alexander L., and Andrew Bennett. 2005. Case Studies and Theory Develop-
ment in the Social Sciences. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
George, Alexander L., and Timothy J. McKeown. 1985. “Case Studies and Theories
of Organizational Decision Making.” In Advances in Information Processing in
Organizations, Vol. 2. ed. Robert F. Coulam and Richard A. Smith, 21–58.
Greenwich, CT: JAI Press.
Hall, Peter A. 2003. “Aligning Ontology and Methodology in Comparative Re-
search.” In Comparative Historical Analysis in the Social Sciences, ed. James Ma-
honey and Dietrich Rueschemeyer, 373–404. New York: Cambridge University
Press.
King, Gary, Robert O. Keohane, and Sidney Verba. 1994. Designing Social Inquiry:
Scientific Inference in Qualitative Research. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University
Press.
Lazarsfeld, Paul F. 1940. “Introduction.” In The Unemployed Man and His Family,
Mirra Komarovsky, ix–xii. New York: Dryden.
Lerner, Daniel. 1958. The Passing of Traditional Society: Modernizing the Middle East.
New York: The Free Press. A somewhat abridged version, which unfortunately
omits some key details, is reprinted in Development: A Cultural Studies Reader,
ed. Susanne Schech and Jane Haggis (Oxford: Blackwell, 2002). This abridged
version is available online in Google Books at: http://tinyurl.com/Lerner-
Grocer-Chief.
Levy, Jack S. 2008. “Counterfactuals and Case Studies.” In The Oxford Handbook of
Political Methodology, ed. Janet M. Box-Steffensmeier, Henry E. Brady, and
David Collier, 627–44. New York: Oxford University Press.
Luebbert, Gregory M. 1991. Liberalism, Fascism, or Social Democracy: Social Classes
and the Political Origins of Regimes in Interwar Europe. New York: Oxford Univer-
sity Press.
Mahoney, James. 2010. “After KKV: The New Methodology of Qualitative Re-
search.” World Politics 62 (1): 120–47.
McAdam, Doug, Sidney Tarrow, and Charles Tilly. 2001. Dynamics of Contention.
New York: Cambridge University Press.
Mill, John Stuart. 1974. A System of Logic. Toronto: University of Toronto Press.
Przeworski, Adam, and Henry E. Teune. 1970. The Logic of Comparative Social In-
quiry. New York: Wiley.
Rogowski, Ronald. 2010. “How Inference in the Social (but Not the Physical) Sci-
ences Neglects Theoretical Anomaly.” In Rethinking Social Inquiry: Diverse
Tools, Shared Standards, 2nd ed., ed. Henry E. Brady and David Collier, 89–97.
Lanham, MD: Rowman and Littlefield.
Schultz, Kenneth A. 2001. Democracy and Coercive Diplomacy. New York: Cam-
bridge University Press.
Sewell, William. 1996. “Three Temporalities: Toward an Eventful Sociology.” In
The Historic Turn in the Human Sciences, ed. Terrence J. McDonald, 245–80. Ann
Arbor: University of Michigan Press.
Skocpol, Theda, Herbert Gans, and Ziad Munson. 2000. “A Nation of Organizers:
The Institutional Origins of American Civic Life.” American Political Science
Review 94 (3) : 527–46.
Tannenwald, Nina. 1999. “The Nuclear Taboo: The United States and the Norma-
tive Basis of Nuclear Non-Use.” International Organization 53 (3): 433–68.
Tilly, Charles. 2001. “Mechanisms in Political Processes.” Annual Review of Political
Science 4: 21–41.
Van Evera, Stephen. 1997. Guide to Methods for Students of Political Science. Ithaca,
NY: Cornell University Press.
Vineberg, Susan. 1996. “Eliminative Induction and Bayesian Confirmation
Theory.” Canadian Journal of Philosophy 26 (June): 257–66.
Waldner, David. 2011. “Process Tracing: Its Promise and Its Problems.” Paper
presented at the Institute for Qualitative and Multi-Method Research, Syra-
cuse University.
Waltz, Kenneth N. 1979. Theory of International Politics. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Weaver, Vesla M. 2007. “Frontlash: Race and the Development of Punitive Crime
Policy.” Studies in American Political Development 21 (Fall): 230–65.
Yin, Robert K. 1984/2008. Case Study Research: Design and Methods, 1st and 4th ed.
Beverly Hills, CA: Sage.
The Teacher: Understanding Process Tracing
.............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
830 PS • October 2011
